Why is my Dog Obsessively Licking Fabric? Tips to Stop This Behavior
Dog Obsessively Licking Fabric Many dog owners have noticed their furry friends developing an obsessive habit of licking fabric. Whether it’s the …
Read Article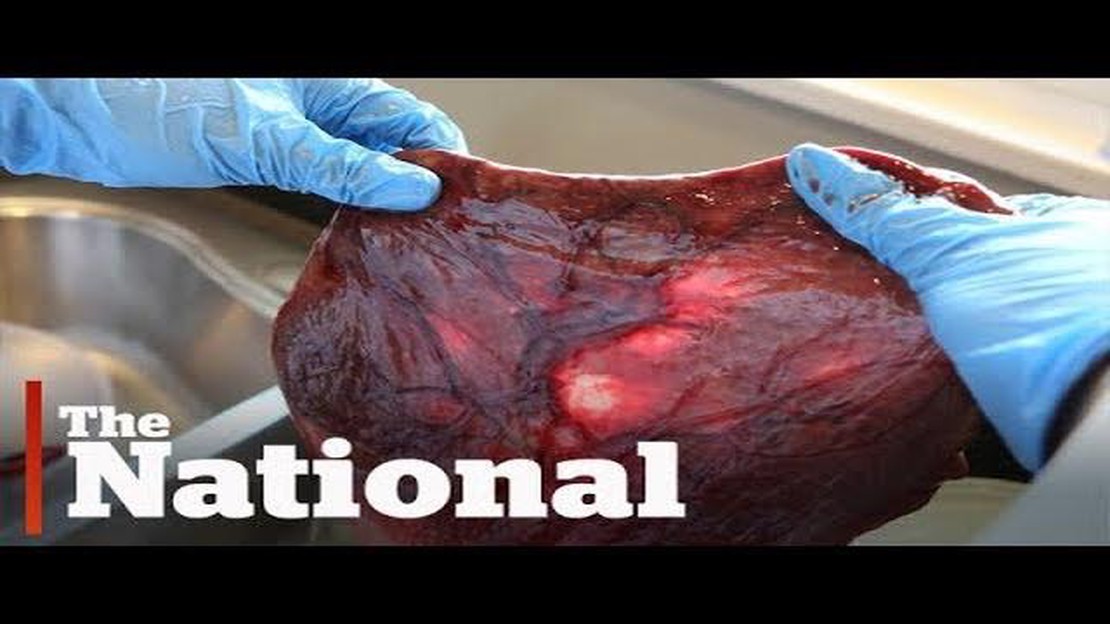
The act of animals eating their own placenta after giving birth may seem peculiar and even repulsive to humans, but it is actually a common practice in many animal species. This behavior, known as placentophagy, has been observed in mammals such as dogs, cats, and even some primates. While the reasons behind this behavior are not completely understood, research suggests that there may be several surprising benefits to consuming the placenta.
One possible reason why animals eat their placenta is to hide the scent of their newborns from potential predators. The placenta contains strong odors that could attract predators, so by consuming it, the mother effectively removes this scent from the environment. This helps to protect her offspring and increase their chances of survival in the wild.
In addition to providing a natural camouflage, the placenta is also rich in nutrients that can benefit the mother. During pregnancy, the placenta acts as a lifeline between the mother and the developing fetus, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen. By consuming the placenta, the mother can replenish her nutrient stores and speed up the recovery process after giving birth.
Furthermore, some studies suggest that placentophagy may have hormonal benefits for the mother. The placenta contains hormones such as oxytocin, which is known to promote feelings of relaxation and bonding. Consuming the placenta may help the mother regulate her hormone levels and reduce the risk of postpartum depression.
While placentophagy is still a subject of ongoing research, it is clear that there are potential benefits to this behavior in the animal kingdom. Understanding why some animals eat their placenta can provide insights into the complex relationships between mothers and their offspring, as well as shed light on the incredible adaptability and survival strategies of different species.
Animals consuming their placenta after giving birth might seem like a strange behavior, but there are actually several unexpected advantages to this practice. While it may not be entirely clear why animals engage in this behavior, researchers have identified some potential benefits.
While these benefits have been observed in various animal species, it is important to note that the practice of consuming placenta is not universal among all animals. Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the reasons behind this behavior and its potential benefits.
As strange as it may seem, the practice of animals eating their placenta after giving birth is actually quite common and has been observed in many different species.
There are several reasons why animals engage in this behavior. For one, consuming the placenta is thought to provide the mother with essential nutrients and hormones that she may have lost during childbirth. The placenta is rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals, all of which can help replenish the mother’s body and aid in the recovery process.
Additionally, some researchers believe that eating the placenta may help stimulate milk production in the mother. This is important for species that have large litters or need to nurse their young for an extended period of time. By consuming the placenta, the mother’s body is triggered to produce more milk, ensuring that her offspring receive the nourishment they need.
Another benefit of eating the placenta is that it helps to keep the birthing area clean and free from predators. By consuming the placenta, the mother eliminates any evidence of her giving birth, reducing the risk of attracting predators to her vulnerable newborns.
Furthermore, it has been suggested that eating the placenta may help mask the scent of the mother’s blood, making it less likely for predators to detect her and her young.
While the practice of animals eating their placenta may seem strange to us, it is important to remember that nature has its reasons for everything. The benefits of this behavior, including increased nutrient intake, improved milk production, and reduced predation risk, make it a natural and beneficial phenomenon.
After giving birth, the female body goes through a range of changes and adjustments. The postpartum period, which lasts for about six weeks, is a critical time for recovering and healing. Eating placenta has been found to provide several benefits that can enhance postpartum recovery.
1. Hormonal Balance: The placenta contains high levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. By consuming the placenta, these hormones are reintroduced into the body, helping to restore hormonal balance and potentially reduce postpartum depression and mood swings.
2. Nutrient Replenishment: Placenta is rich in essential nutrients, including iron, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12. These nutrients are crucial for replenishing the mother’s nutritional stores, which may have been depleted during pregnancy and childbirth. Adequate nutrient levels support the healing process and boost energy levels.
3. Faster Healing and Reduced Bleeding: The placenta contains growth factors and stem cells that can stimulate tissue regeneration and accelerate the healing process. Consuming placenta may help reduce postpartum bleeding, speed up wound healing, and promote overall recovery from childbirth.
4. Increased Breast Milk Production: Some studies suggest that eating placenta may increase breast milk production. The hormones present in placenta, such as prolactin, could potentially stimulate milk production, ensuring an adequate supply for the newborn.
Read Also: When Do Puppies Stop Having Accidents: A Comprehensive Guide
5. Pain Relief: Placentophagy has been linked to pain relief and reduced discomfort after childbirth. The release of endorphins and oxytocin, which are present in the placenta, can help alleviate postpartum pain and promote relaxation.
While the practice of eating placenta is not widely accepted or understood, it is gaining popularity among some new mothers. Before considering placenta consumption, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure the safety and proper handling of the placenta.
Read Also: Iams Dog Food: How Much to Feed? – Expert Guide and Feeding Recommendations
Eating the placenta has been reported to promote lactation in some animals. The placenta contains hormones, such as prolactin and oxytocin, which are essential for milk production and the release of milk from the mammary glands. By consuming the placenta, animals may be able to boost the production of these hormones, leading to increased milk supply and better breastfeeding success.
In addition to supporting lactation, eating the placenta is thought to enhance bonding between the mother and her offspring. The act of consuming the placenta may release endorphins and oxytocin, which are hormones associated with pleasure and maternal attachment. This can help the mother feel more connected to her young and strengthen the mother-infant bond.
Furthermore, some studies in humans have suggested that consuming the placenta may have similar effects. While more research is needed to fully understand the impact on lactation and bonding in humans, some women believe that eating their placenta after childbirth can help them establish breastfeeding and feel more emotionally connected to their baby.
It’s important to note that the practice of eating the placenta, also known as placentophagy, is not universally accepted or recommended by medical professionals. The potential benefits described here are based on anecdotal evidence and observations in certain animal species. If you’re considering placenta consumption, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to weigh the potential risks and benefits for your specific situation.
The placenta contains a variety of essential nutrients that are beneficial to the mother and her offspring. These nutrients include:
Eating the placenta allows the mother to conveniently and naturally replenish these essential nutrients, which may have been depleted during the birthing process.
Furthermore, the placenta is also a rich source of hormones such as oxytocin and prolactin. Oxytocin is known as the “love hormone” and is responsible for bonding and maternal behaviors. Prolactin plays a crucial role in promoting milk production and breastfeeding.
By consuming the placenta, a mother can potentially benefit from the hormonal balance and support the bonding process with her newborn.
The consumption of placenta by animals is a behavior that has been observed in various species across different taxonomic groups. While the exact reasons for this behavior are still not fully understood, there are several plausible evolutionary explanations that have been proposed.
It is important to note that while these explanations provide some insight into the possible evolutionary origins of placenta consumption, more research is needed to fully understand the reasons behind this behavior in different animal species. Additionally, it is worth considering that the reasons for placenta consumption may vary among species, highlighting the complexity of this behavior.
The placenta is an organ that develops during pregnancy and is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus.
Some animals eat their placenta because it provides them with important nutrients and hormones that can help with their recovery after giving birth.
Eating the placenta can help stimulate milk production, reduce postpartum depression, and provide important nutrients and hormones that can aid in the recovery process for the mother.
Many mammals, including dogs, cats, and rodents, commonly eat their placenta.
The safety of eating the placenta for humans is still a topic of debate among medical professionals. Some believe that it can provide benefits, while others are skeptical and recommend against it. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering consuming the placenta.
There are potential risks associated with eating the placenta, such as infections and exposure to toxins. It is important to properly prepare and cook the placenta if you choose to consume it to minimize these risks.
Dog Obsessively Licking Fabric Many dog owners have noticed their furry friends developing an obsessive habit of licking fabric. Whether it’s the …
Read ArticleRubbing Coconut Oil On Dog Coconut oil has gained immense popularity in recent years for its numerous health benefits. But did you know that it can …
Read ArticleDream Of Stepping In Dog Poop Stepping in dog poop is an unpleasant experience that can ruin your day. Not only does it make a mess on your shoes and …
Read ArticleHow Many Days Can A Shih Tzu Take A Bath After Giving Birth Shih Tzus are a popular breed known for their long, flowing coats and adorable looks. They …
Read ArticleDoes The Dog Die In The Platform Netflix’s “The Platform” has caused quite a stir since its release, with viewers eagerly discussing its dark themes …
Read ArticleDog Won’t Pee With Cone On If your dog is wearing a cone and refuses to pee, it can be a frustrating and concerning situation. Fortunately, there are …
Read Article