How Safe Are Bath And Body Works Candles for Dogs? Find Out Here
Are Bath And Body Works Candles Safe For Dogs If you’re a dog owner, you know that your furry friend is part of the family. You want to ensure their …
Read Article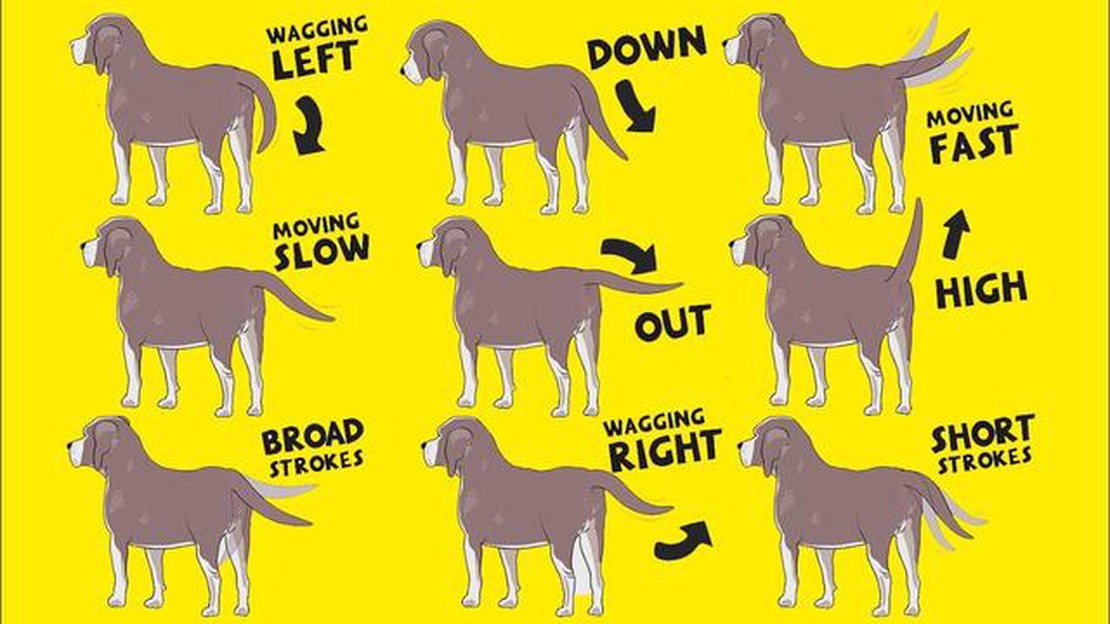
If you have noticed that your dog is constantly holding its tail to one side, it may be concerning and you might be wondering what could be causing this behavior. There can be several possible causes for this, and understanding them can help you find the best solution for your furry friend.
1. Injury or Trauma: One of the most common reasons for a dog holding its tail to one side is an injury or trauma. Your dog may have experienced a fall, hit, or any other form of physical injury that is causing discomfort or pain in its tail. It’s important to carefully examine your dog’s tail for any signs of swelling, bruising, or tenderness. If you suspect an injury, it’s best to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
2. Tail Infection: Another possible cause for your dog holding its tail to one side could be an infection. Tail infections can be caused by bacteria, yeast, or parasites. Common symptoms of a tail infection include redness, swelling, discharge, and a foul odor. If you suspect a tail infection, it’s important to take your dog to the vet for an examination and appropriate treatment.
3. Muscle or Nerve Damage: Muscle or nerve damage can also be a reason for your dog holding its tail to one side. This can occur due to repetitive strain, excessive exercise, or even certain medical conditions. If you notice that your dog’s tail is limp or appears weak, it’s advisable to seek veterinary attention to determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
4. Behavioral Issues: In some cases, a dog holding its tail to one side could be a behavioral issue. Dogs may display this behavior as a result of anxiety, fear, or stress. If you suspect that your dog’s tail-holding behavior is due to behavioral issues, consult a professional dog trainer or animal behaviorist to address the underlying problem.
“Understanding the possible causes for your dog holding its tail to one side can help you find the best solution for your furry friend.”
In conclusion, if you notice your dog holding its tail to one side, it’s important to closely observe their behavior and physical condition. If you notice any concerning symptoms or behaviors, it’s always best to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, your dog’s health and well-being should always be a top priority.
If you have noticed that your dog is holding its tail to one side, it may be a sign of an underlying issue. Here are some possible causes and solutions for this behavior.
In any case, it is important to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. They will be able to assess your dog’s condition and recommend the best course of action.
If your dog is holding its tail to one side, it could be due to a tail injury or trauma. Dogs’ tails are vulnerable to various injuries, including fractures, sprains, and dislocations. It is essential to identify and treat any tail injuries promptly to avoid further complications.
Possible causes of tail injury or trauma:
Signs and symptoms of tail injury or trauma:
Treatment options:
If you suspect that your dog has a tail injury or trauma, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian. The vet will perform a thorough examination and may recommend the following treatment options:
In some cases, follow-up appointments or physical therapy may be necessary to monitor the healing progress and ensure proper recovery.
Prevention:
To prevent tail injuries or trauma in dogs, take the following precautions:
Read Also: Spray Bottle Training Dog: Effective Techniques and Tips for Behavior Correction
Remember, early detection and proper treatment are essential for your dog’s well-being. If you suspect a tail injury or trauma, consult with a veterinarian for the best course of action.
If your dog is holding its tail to one side, it could be a sign of muscular or neurological conditions. Some potential causes include:
If you suspect that your dog’s tail deviation is due to a muscular or neurological condition, it is essential to consult with a veterinarian. They can perform a thorough examination, diagnose the underlying cause, and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Anal gland issues can be a common cause of why a dog holds its tail to one side. These small glands are located on either side of a dog’s anus and can become impacted or infected, causing discomfort and pain.
If you notice your dog constantly licking or biting its tail, or if you see your dog dragging its bottom along the ground, it may be a sign of anal gland issues. Other symptoms can include a foul odor, redness or swelling around the anal area, and difficulty defecating.
To address anal gland issues, it is important to take your dog to a veterinarian. They can examine the glands, manually express them if necessary, and provide any necessary treatment such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications.
Read Also: Dog Emoticons For iPhone: Express Yourself with Adorable Dog Icons
To prevent future occurrences of anal gland issues, maintaining a high-fiber diet can help promote regular bowel movements and proper gland function. Regular exercise can also help your dog maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce the risk of gland impaction.
In some cases, frequent anal gland issues may require more invasive treatments such as surgery to remove or modify the affected glands. Your veterinarian will be able to determine the best course of action based on the specific needs of your dog.
Remember, if you suspect your dog is experiencing anal gland issues, it is always best to consult with a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
If your dog is holding its tail to one side and displaying other symptoms such as frequent scratching or shaking of the head, it may be a sign of an ear infection or ear mites.
Ear infections can occur due to a variety of reasons, including bacteria, yeast, allergies, or trapped moisture. Ear mites, on the other hand, are tiny parasites that often infest the dog’s ears and cause irritation.
Common symptoms of ear infections or ear mites:
If you suspect that your dog may have an ear infection or ear mites, it is important to seek veterinary attention. A veterinarian can examine your dog’s ears and determine the underlying cause of the symptoms. They may recommend treatments such as ear drops, oral medication, or an ear cleaning solution.
Preventing ear infections or ear mites:
By taking proactive measures to maintain your dog’s ear health, you can help prevent ear infections or ear mites and ensure your furry friend remains comfortable and happy.
Sometimes dogs may hold their tails to one side due to behavioral reasons or anxiety. This behavior can be a sign of stress, fear, or a traumatic event that has caused your dog to feel uneasy. Here are some possible reasons and solutions for this behavior:
Remember, if your dog continues to hold their tail to one side despite your efforts, it is always recommended to consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist. They can provide you with additional guidance and support to help address your dog’s specific needs and ensure their overall well-being.
There can be various reasons why your dog is holding its tail to one side. It could indicate an injury or pain in the tail or lower back. It could also be a sign of an infection or irritation in the anal area. Additionally, it could be a behavioral issue such as fear or anxiety. It’s best to consult with a veterinarian to determine the exact cause and appropriate solutions.
There are several possible causes for a dog holding its tail to one side. It could be due to an injury to the tail or lower back, such as a sprain or strain. It could also be a sign of an infection or irritation in the anal area. In some cases, it may be a behavioral issue related to fear or anxiety. It’s important to have your dog evaluated by a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause.
If your dog is holding its tail to one side and you suspect it may be due to pain, look for other signs such as changes in behavior, difficulty walking or standing, flinching when the tail or lower back is touched, or a decrease in appetite. However, the best course of action is to bring your dog to a veterinarian who can perform a physical examination and potentially recommend further diagnostic tests to identify the source of the pain.
If you notice that your dog is holding its tail to one side, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian. The veterinarian will be able to examine your dog and determine the cause of this behavior. They may recommend further tests or treatments depending on the underlying cause. It’s always better to be on the safe side and seek professional advice when it comes to your dog’s health.
Yes, anxiety or fear can potentially cause a dog to hold its tail to one side. Some dogs may exhibit this behavior as a response to stressful situations or as a sign of fear or anxiety. If you suspect this is the case, it may be helpful to consult with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist who can provide guidance on how to help your dog overcome their anxiety or fear and stop holding their tail to one side.
Are Bath And Body Works Candles Safe For Dogs If you’re a dog owner, you know that your furry friend is part of the family. You want to ensure their …
Read ArticleDog Swollen Lymph Nodes Home Remedies Is your furry friend suffering from swollen lymph nodes? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. Our natural …
Read ArticleWhat Happens If A Dog Eats Allergy Pills Allergy medication is commonly used to treat various allergic reactions in humans, but what happens if your …
Read ArticleWhy Does My Dog Move From Room To Room At Night Dogs have a range of unusual behaviors and quirks that can leave even the most experienced pet owner …
Read ArticleHow Long It Takes For Trazodone To Work For Sleep Many people struggle with sleep problems, whether it’s difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep …
Read ArticleDog Coughing And Gagging White Foam Watching your dog coughing and gagging can be a distressing experience for any pet owner. While occasional …
Read Article