Is Playdough Toxic To Dogs: What Every Dog Owner Should Know
Is Playdough Toxic To Dogs Playdough is a popular toy for children, known for its soft and moldable texture. However, if you’re a dog owner, you may …
Read Article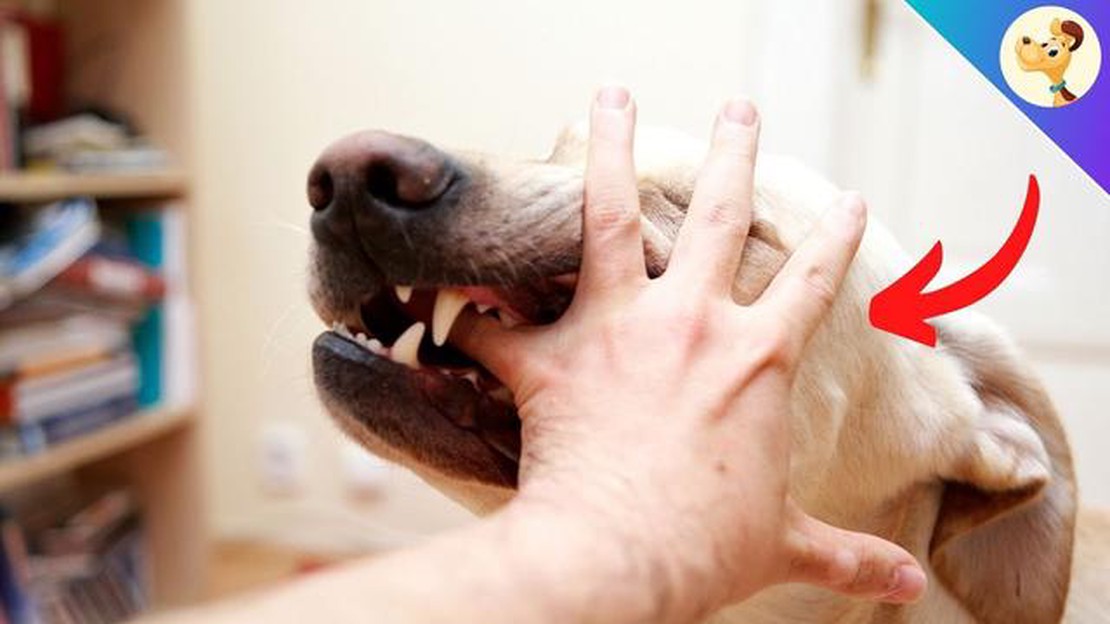
Dogs are known for their unique behaviors and it is not uncommon for dog owners to witness their furry companions snapping their jaws. This interesting behavior may seem concerning or aggressive to some, but it is important to understand that there are various reasons why dogs exhibit this behavior.
One of the most common reasons why dogs snap their jaws is to communicate. Just like humans use gestures and facial expressions, dogs use body language to express themselves. Snapping their jaws can be a way for dogs to convey their emotions or intentions. For example, a dog may snap their jaws as a warning sign to communicate that they are feeling stressed or uncomfortable in a certain situation.
Another reason why dogs snap their jaws is because of their natural instincts. Dogs are descendants of wolves, and wolves use jaw snapping as a part of their communication and social hierarchy. This behavior can be seen when dogs are playing or interacting with other dogs. It is their way of asserting dominance or indicating boundaries.
It is important to note that not all jaw snapping is a sign of aggression or dominance. Sometimes, dogs may snap their jaws out of excitement or as a way to release excess energy. This behavior can be seen during playtime or when dogs are anticipating something, such as going for a walk or receiving a treat.
In conclusion, dogs snap their jaws for various reasons, including communication, natural instincts, and excitement. It is crucial for dog owners to understand their pet’s body language and overall behavior to ensure a happy and healthy relationship with their furry friend.
Dogs are known for their wide range of behaviors, and one of those behaviors includes snapping their jaws. This behavior can be seen in various situations and can have different meanings depending on the context.
1. Communication: Dogs may snap their jaws as a form of communication. It can be a way for them to express their emotions, such as excitement, frustration, or aggression. For example, when a dog is excited to see their owner, they may snap their jaws as a way of expressing their joy.
2. Play: Dogs often snap their jaws during play. It’s a common behavior during rough play or when playing with toys. When dogs play with each other, they may use their jaws to playfully nip or bite at each other. This behavior is usually harmless and is their way of engaging in play.
3. Warning or Threat: Sometimes, dogs may snap their jaws as a warning or threat. This behavior can be seen when a dog is feeling threatened, defensive, or territorial. By snapping their jaws, they are trying to intimidate or ward off potential threats.
4. Frustration or Impatience: Dogs may also snap their jaws when they are frustrated or impatient. This behavior can be seen when a dog is waiting for something, like food or attention, and they are getting impatient. It’s their way of expressing their frustration or desire for something.
5. Hunting Instinct: Dogs have a natural hunting instinct, and snapping their jaws can be a manifestation of that instinct. When they see something that triggers their prey drive, such as a squirrel or a moving object, they may snap their jaws in anticipation.
It’s important to note that the context and body language of the dog should be taken into consideration when interpreting why they are snapping their jaws. If you are unsure about the meaning behind a dog’s behavior, it’s always best to consult with a professional dog behaviorist or trainer.
Understanding canine behavior is essential for anyone who interacts with dogs, whether as a pet owner, a professional dog trainer, or a veterinarian. Dogs are complex creatures with their own unique set of instincts, emotions, and communication methods. By gaining a deeper understanding of their behavior, we can not only improve our relationships with dogs but also ensure their well-being.
Here are a few reasons why understanding canine behavior is important:
Overall, understanding canine behavior is crucial for creating a harmonious and fulfilling relationship with dogs. It allows us to train them effectively, prevent behavioral issues, provide better health care, and strengthen our bond with them. By investing time and effort in understanding their behavior, we can ensure that our interactions with dogs are positive, safe, and enjoyable for all parties involved.
Dogs are social animals that have evolved to communicate and interact with each other and with humans. They have developed a range of natural instincts and behaviors that help them navigate the social world and express their needs and emotions.
One of the ways dogs communicate is through body language. They use a combination of facial expressions, posture, and vocalizations to convey their intentions and emotions. For example, a dog may wag its tail when it is happy or excited, while a raised and rigid tail can indicate aggression or fear.
In addition to body language, dogs also use vocalizations to communicate. They can bark, growl, howl, or whimper to express different emotions and needs. Barking, for example, can be a form of alerting others to potential danger or a way to seek attention or play.
Another important aspect of canine communication is scent marking. Dogs have a highly developed sense of smell and can use their urine or feces to mark territory and communicate with other dogs. This behavior is often seen in male dogs, but females can also engage in scent marking.
Understanding these natural instincts and communication methods is crucial for dog owners and anyone who interacts with dogs. By paying attention to a dog’s body language, vocalizations, and scent marking behaviors, we can better understand their needs and emotions, and build a stronger bond with our canine companions.
Dogs are known for their protective behavior towards their owners and their territory. This behavior is rooted in their natural instincts and serves as a way to defend against potential threats.
Protective behavior: Dogs have a deep instinct to protect their owners and the members of their pack. This behavior can manifest in various ways, such as barking, growling, or even snapping their jaws. These protective instincts are usually triggered in response to perceived threats, whether it be a stranger approaching their owner or an unfamiliar noise in their environment.
Territoriality: Dogs are also highly territorial animals. They have a strong instinct to mark and defend their territory, which can include their homes, yards, or even their favorite toys. This territorial behavior is often seen when another animal or person enters their space, and the dog may resort to snapping their jaws as a warning sign or a display of dominance.
It’s important to note that while protective behavior and territoriality are natural instincts in dogs, they can also be influenced by factors such as socialization and training. Dogs that have been well-socialized and trained may be less likely to exhibit excessive protective behavior or territoriality. However, it is still essential for owners to understand these instincts and take appropriate measures to manage and control their dog’s behavior.
Managing protective behavior and territoriality:
Read Also: How to Boil Chicken Breast for Dogs: A Healthy and Easy Cooking Method
By understanding the reasons behind dogs snapping their jaws, particularly in relation to protective behavior and territoriality, owners can better manage and address these behaviors in their pets. With the right training and socialization, dogs can learn to express their protective instincts in a more controlled and acceptable manner.
Dogs have a natural instinct to play, and it is a behavior that serves several important purposes. Play helps dogs to develop social skills, improve physical coordination, and release pent-up energy. When dogs engage in play, they often exhibit various behaviors that may include snapping their jaws.
Snapping their jaws during play is commonly seen as a form of communication between dogs. It is often a playful gesture, showing excitement and anticipation. Dogs may snap their jaws as a way to get the attention of their playmate or to initiate a game of chase or tug-of-war.
It is important to note that snapping their jaws during play is usually not aggressive behavior. It is a way for dogs to express their enthusiasm and eagerness to engage in play. However, it is crucial for dog owners to monitor their dog’s behavior and intervene if play becomes too rough or aggressive.
Read Also: Do Moles Eat Dog Poop: Exploring the Relationship Between Moles and Canine Waste
Dogs may also snap their jaws during play as a way to signal their intention to play-bite. Play-biting is a common behavior among dogs and is their way of mimicking a bite without causing harm. During play, dogs may gently bite or snap their jaws without actually making contact with the other dog or object.
Playful behavior and excitement can also lead to snapping their jaws in other situations apart from play. For example, dogs may snap their jaws when they are excited to see their owner, when they anticipate receiving a treat or toy, or when they are engaged in an enjoyable activity such as a walk or game of fetch.
It is important for dog owners to recognize the difference between playful snapping and aggressive snapping. Aggressive snapping is usually accompanied by other signs of aggression such as growling, raised hackles, and stiff body posture. If a dog is exhibiting aggressive snapping behavior, it is crucial to seek professional help from a veterinarian or animal behaviorist to address the underlying issue.
In conclusion, dogs snapping their jaws during play or moments of excitement is a normal behavior and a way for them to communicate and express their enthusiasm. As responsible dog owners, it is important to understand and recognize the difference between playful snapping and aggressive behavior to ensure the safety and well-being of both dogs and humans.
When a dog snaps its jaws, it can be a sign of aggression or fear-related behavior. Understanding the reasons behind this behavior can help dog owners and trainers address the underlying issues and prevent potential harm.
Aggression:
Dogs are capable of showing aggression in response to various stimuli, including perceived threats, territorial disputes, resource guarding, or fear. Snapping their jaws can be a warning sign that the dog is feeling threatened or preparing to defend itself.
It is important to note that aggression can arise from a variety of factors, such as poor socialization, previous traumatic experiences, or genetic predisposition. Identifying the triggers for aggression and addressing them through proper training and behavior modification can help reduce snapping behavior.
Fear-related snapping:
Fear can also lead to snapping behavior in dogs. When a dog feels scared or threatened, it may resort to snapping as a defensive reaction. This behavior is often accompanied by other signs of fear, such as cowering, growling, or showing a submissive posture.
Understanding the cause of fear in a dog is crucial in managing their behavior. It is essential to provide a safe and comforting environment for the dog and gradually expose them to feared stimuli in a controlled and positive manner. This can help desensitize the dog and reduce their fear-related snapping behavior.
Training and socialization:
In both cases of aggression and fear-related snapping, proper training and socialization are essential. Training should focus on teaching the dog appropriate behaviors and reinforcing positive actions. Positive reinforcement techniques, such as reward-based training, can help redirect the dog’s behavior and promote desired responses.
Additionally, socialization plays a crucial role in preventing snapping behavior. By exposing the dog to various people, animals, and environments from an early age, they can learn to feel more comfortable and confident in different situations.
Consulting a professional:
If a dog’s snapping behavior becomes a persistent issue or poses a risk to themselves or others, it is recommended to seek the guidance of a professional dog trainer or behaviorist. These experts can provide personalized advice and assistance in addressing the underlying issues and ensuring the safety and well-being of both the dog and those around them.
Dogs may snap their jaws due to various medical conditions and dental issues. These can be painful and uncomfortable for dogs, leading to abnormal behaviors such as snapping their jaws. Some common conditions and issues that may cause dogs to snap their jaws include:
If you notice your dog frequently snapping their jaws, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause. A veterinary examination, dental cleaning, or additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to identify and treat the medical condition or dental issue causing the behavior.
Dogs may snap their jaws as a warning sign or as a form of communication. It can also be a response to excitement or frustration.
Jaw snapping can be a normal behavior in dogs, especially during play or when they are trying to get your attention. However, it can also be a sign of aggression or fear.
If your dog snaps its jaws while displaying other signs of aggression, such as growling, showing teeth, or stiff body posture, it is likely a behavior associated with aggression. It is important to seek professional help to address this issue.
If your dog snaps its jaws at you or other people, it is important to understand the underlying cause of this behavior. Consulting with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can help identify the cause and provide appropriate training techniques to address it.
Yes, snapping jaws can be a sign of pain in dogs. If you notice your dog snapping its jaws along with other signs of discomfort, such as whining, limping, or avoiding certain movements, it is recommended to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Is Playdough Toxic To Dogs Playdough is a popular toy for children, known for its soft and moldable texture. However, if you’re a dog owner, you may …
Read ArticleDo Vets Drug Test Dogs As responsible pet owners, it’s important for us to ensure the health and well-being of our furry friends. But have you ever …
Read ArticleCan I Euthanize My Dog With Gabapentin Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat nerve pain and seizures in humans. However, it has …
Read ArticleMost Expensive Dog Food When it comes to your furry friend, only the best will do. Treat your beloved pooch to the finest cuisine with our handpicked …
Read ArticleLeft Freshpet Out Overnight Leaving Freshpet out overnight can have consequences for both the freshness of the food and the health of your pet. …
Read ArticleNeutered Dogs Can Have Sex One of the most common questions dog owners may have is whether neutered dogs can still have sex. Neutering is a surgical …
Read Article