Get Your Allegheny County Treasurer Dog License Online Today
Allegheny County Treasurer Dog License In Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, it is a requirement to have a dog license for any canine companion. Not only …
Read Article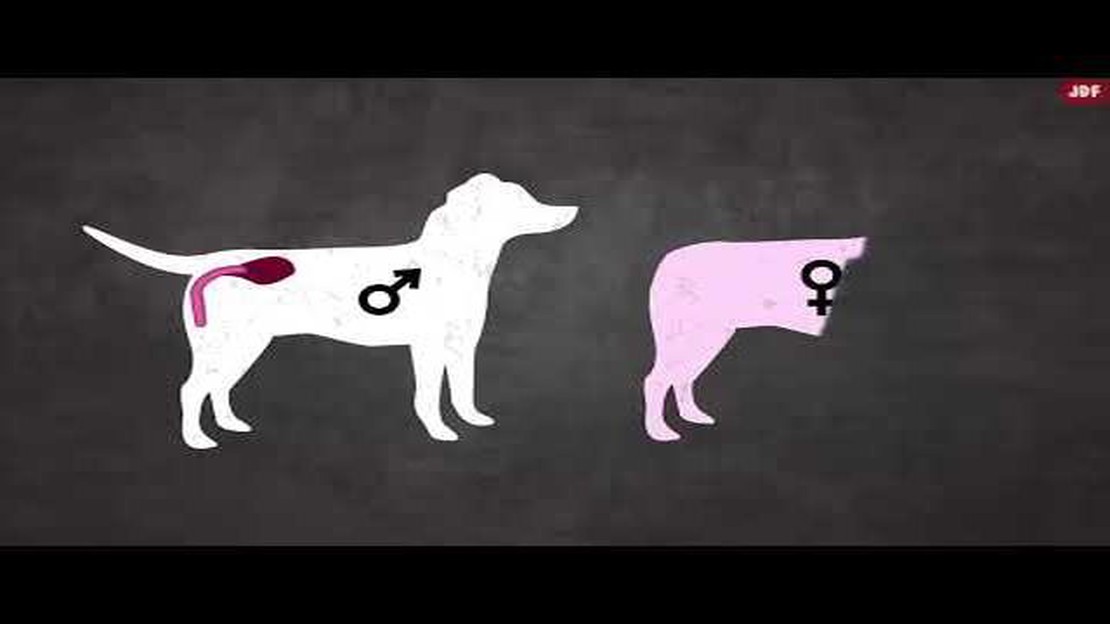
Why Do Dogs’ Bums Get Stuck Together? The Surprising Reasons Behind This Behavior
Have you ever wondered why dogs’ bums get stuck together? It’s a peculiar behavior that can leave pet owners both confused and concerned. While it may seem strange to us, there are actually several reasons why dogs engage in this behavior.
One of the main reasons behind dogs’ bums getting stuck together is mating. When a male dog mates with a female dog, the male’s penis swells inside the female’s vagina, creating a biological lock known as a “tie.” This tie is a natural part of the mating process and can last from a few minutes to over an hour. During this time, the two dogs are physically connected, causing their bums to appear stuck together.
Another reason for dogs’ bums getting stuck together is the scent of other dogs. Dogs have glands near their anus, known as anal glands, which produce a strong and distinct odor. When dogs sniff each other’s bums, they’re actually gathering information about the other dog, including their gender, health, and reproductive status. Sometimes, dogs may get too close during this sniffing behavior, which can result in their bums momentarily getting stuck together.
It’s important to note that while dogs’ bums getting stuck together can be a normal behavior, it should also be monitored. If the tie lasts for an unusually long time or if either dog appears distressed or in pain, it’s recommended to seek veterinary assistance. Additionally, if your dog frequently engages in this behavior with other dogs, it may be a sign of an underlying issue, such as an infection or reproductive problem.
In conclusion, the behavior of dogs’ bums getting stuck together may seem unusual, but it has logical explanations. Mating and scent-related interactions with other dogs are the primary reasons behind this behavior. As responsible pet owners, it’s essential to be aware of our dogs’ behavior and seek professional advice if any concerns arise.
Understanding the basics of canine reproduction is important for dog owners and breeders alike. Whether you are considering breeding your dog or simply curious about the process, this article will provide you with an overview of the key aspects of canine reproduction.
1. Estrus Cycle: Female dogs undergo a reproductive cycle called the estrus cycle or the heat cycle. This cycle typically occurs every six to twelve months, depending on the breed and individual dog. During this time, the female dog is fertile and capable of mating and becoming pregnant.
2. Signs of Heat: There are several signs that indicate a female dog is in heat. These signs include a swollen vulva, a bloody discharge, increased urination, and a change in behavior. Male dogs may also exhibit increased interest in the female during this time.
3. Mating: Canine mating usually occurs naturally, with the male mounting the female from behind. The mating process can be quite quick, lasting only a few minutes. It’s important to note that dogs are capable of mating with different partners during their heat cycle.
4. Pregnancy: If mating is successful, the female dog may become pregnant. Pregnancy in dogs lasts approximately 63 days, but this can vary slightly. During pregnancy, the female dog may display changes in appetite, behavior, and physical appearance.
5. Whelping: Whelping is the term used to describe the process of giving birth in dogs. It typically occurs around nine weeks after mating. During this time, the female dog will experience contractions and will give birth to a litter of puppies. It’s important to provide the mother dog with a comfortable and quiet environment during this process.
6. Puppy Development: After birth, the puppies will rely on their mother for nourishment and care. They will grow and develop rapidly during the first few weeks of their lives. It’s essential to provide proper nutrition and veterinary care to ensure the health and well-being of the mother dog and her puppies.
Conclusion: Canine reproduction is a complex process, and understanding the basics is essential for dog owners and breeders. By being aware of the estrus cycle, signs of heat, mating process, pregnancy, whelping, and puppy development, you can ensure the health and success of your dog’s reproductive journey.
Dogs’ reproductive behavior is influenced by a variety of hormonal changes that occur in their bodies. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the dog’s reproductive cycle and behavior. Understanding the role of hormones can provide insights into why dogs’ bums get stuck together and other related behaviors.
Estrus Cycle:
Female dogs go through a reproductive cycle known as the estrus cycle or heat cycle. This cycle is regulated by the hormones estrogen and progesterone. During the estrus cycle, a female dog is sexually receptive and can conceive. The male dogs are capable of detecting the pheromones released by the female dogs during this phase, which leads to the mounting behavior and the sticking together of their bums.
Testosterone:
Male dogs produce testosterone, a hormone that plays a crucial role in their reproductive behavior. Testosterone influences the dog’s territorial and dominance instincts and increases their urge to mount and mate. It also contributes to the male dog’s ability to detect and respond to the pheromones released by the female dogs in heat.
Pheromones:
Pheromones are chemical substances released by dogs that play a crucial role in their reproductive behavior. Female dogs release pheromones during their heat cycle to attract male dogs. Male dogs can sense these pheromones, which triggers their mating behavior, including mounting and sticking together of bums.
Behavioral Changes:
Changes in hormone levels during the estrus cycle can also lead to various behavioral changes in female dogs. Some female dogs may display increased affection, restlessness, frequent urination, and changes in their vocalizations. Male dogs may become more territorial, aggressive, and hyperactive during the breeding season, influenced by changes in hormone levels.
Medical Considerations:
Hormonal imbalances can sometimes affect a dog’s reproductive behavior. For example, in cases of excessive testosterone production in male dogs, aggressive or abnormal mating behaviors may be observed. It is important to consult with a veterinarian if there are concerns regarding a dog’s reproductive behavior or hormonal imbalances.
In conclusion, hormonal changes have a significant impact on dogs’ reproductive behavior. The hormones estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone play crucial roles in regulating the estrus cycle, mounting behavior, and the sticking together of bums. Understanding these hormonal influences can help dog owners better understand and manage their pets’ reproductive behavior.
Read Also: Reasons Your Dog is Not Pooping on a Bland Diet: Common Causes and Solutions
The mating process in dogs involves several steps and behaviors that are essential for reproduction. When two dogs mate, they engage in a series of instinctive actions that ensure successful breeding and fertility.
1. Attraction: Before mating, there is an attraction phase where the male and female dogs show signs of interest in each other. They may sniff each other, wag their tails, and exhibit playful behavior.
Read Also: How Much Does A Caregiver Get In The USA - Salary Guide
2. Mounting: Once the attraction phase is established, the male dog will mount the female dog from behind. This is a natural behavior and is a part of the mating instinct. The male’s mounting stimulates the female and prepares her for breeding.
3. Locking: After the male mounts the female, a phenomenon called “tying” or “locking” occurs. This is when their genitalia becomes interlocked, and they are physically connected during the act of mating. This locking can last from a few minutes to over an hour and is necessary for successful insemination.
4. Ejaculation: During the locking phase, the male dog will ejaculate semen into the female dog’s reproductive tract. The semen contains sperm cells that will fertilize the female’s eggs, leading to potential pregnancy.
5. Post-Mating Behavior: After the male dog ejaculates, they typically release from the female. The dogs may separate and go their separate ways or continue to stay close to each other for a short period. The female may also show signs of disinterest in the male after mating.
6. Fertilization: If the mating is successful and the female is at the right point in her reproductive cycle, fertilization can occur. The sperm cells travel to the female’s eggs, and if fertilization occurs, the female dog may become pregnant and give birth to a litter of puppies.
It’s important to note that not all mating attempts result in successful reproduction. Factors such as timing, fertility, and overall health can influence the chances of fertilization and pregnancy.
In conclusion, the mating process in dogs involves attraction, mounting, locking, ejaculation, and post-mating behavior. These behaviors and actions are instinctive and essential for successful reproduction in dogs.
When dogs’ bums get stuck together, it can be a confusing and somewhat awkward sight for many pet owners. This behavior, commonly known as “butt sticking,” is often observed during the mating process, but it can also occur in non-sexual contexts. Understanding the physical mechanics behind this behavior can shed light on why it happens.
One of the main reasons why dogs’ bums get stuck together is due to the shape of their reproductive organs. Male dogs have a penis that becomes engorged and expands during arousal. This expansion creates a natural mechanism that helps facilitate mating by ensuring proper positioning and preventing premature separation.
Similarly, female dogs have a structure known as the vulva, which also undergoes changes during mating. The female’s vulva swells and becomes more prominent, allowing for proper alignment with the male’s penis. This swelling further enhances the mating process and helps ensure successful reproduction.
During mating, when the male’s penis is inserted into the female’s vulva, the engorgement and expansion of both organs create a tight seal. This seal is achieved through a combination of physiological processes, including the swelling of surrounding tissues and the locking of specialized structures. Once the seal is formed, the dogs’ bums can become temporarily stuck together.
It is important to note that this behavior is completely natural and serves an essential purpose in the reproductive cycle of dogs. The duration of the “butt sticking” can vary, with some dogs being stuck together for just a few minutes, while others may remain connected for up to an hour.
After the mating process is completed, a male dog’s penis will deflate, and the female’s vulva will return to its normal state. This will allow the dogs to separate naturally and resume their normal activities.
If you observe dogs getting their bums stuck together outside of a mating context, it could be a sign of health issues, such as a medical condition called “priapism” in males or an infection in females. In such cases, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, the physical mechanics behind why dogs’ bums get stuck together during mating involve the engorgement and expansion of the male’s penis and the swelling and alignment of the female’s vulva. This natural process ensures proper positioning and increases the chances of successful reproduction. Understanding these mechanisms can help pet owners gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the canine reproductive system.
When dogs mate, there is more than just the physical act of reproduction taking place. The psychological aspect of bonding and dominance also plays a significant role in canine mating behavior. Dogs are social animals with complex social hierarchies, and these hierarchies can influence their mating behavior.
One key element of mating behavior in dogs is the establishment of dominance. Dominance is a concept that refers to the social order or hierarchy within a group of animals. In a mating context, dominance can play a role in determining which dog will be in the position of dominance during the mating process.
During mating, dogs engage in a behavior known as “locking,” where the male’s penis swells inside the female’s vagina, creating a physical connection. This locking behavior can last for a few minutes to over an hour. The psychological aspect of this behavior is related to dominance. The male dog’s ability to maintain the lock demonstrates his strength and dominance over the female.
Additionally, the locking behavior serves as a way for dogs to strengthen their bond. Through physical connection and the release of various hormones during mating, dogs experience a sense of intimacy and connection. This bonding process helps establish a stronger relationship between the mating partners.
It is important to note that not all dogs engage in locking behavior during mating, and some breeds are more prone to this behavior than others. Factors such as breed, individual temperament, and the dynamics of the specific mating pair can influence the occurrence of locking.
In conclusion, the psychological aspect of bonding and dominance plays a significant role in canine mating behavior. Through locking, dogs establish dominance and strengthen their bond with their mating partner. This behavior is part of the complex social dynamics that exist within the canine world.
Dogs’ bums can get stuck together due to a phenomenon called “mating lock” or “copulatory tie.” This occurs when the male dog’s penis swells inside the female dog’s vagina during mating, making it difficult for them to separate.
The duration of dogs’ bums being stuck together can vary, but it typically lasts for around 10 to 30 minutes. During this time, the male dog’s penis remains inside the female dog’s vagina, allowing the successful transfer of sperm.
If dogs are unable to unlock their bums after mating, it is important for human intervention to separate them. A veterinarian may need to be consulted, as forcing them apart can cause injury. Failure to separate them can lead to serious complications and potential harm to both dogs.
Dogs may get stuck together even after successful mating due to the natural process of the copulatory tie. This helps ensure that the male dog’s sperm is properly transferred to the female dog’s reproductive tract for a higher chance of successful fertilization.
Allegheny County Treasurer Dog License In Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, it is a requirement to have a dog license for any canine companion. Not only …
Read ArticleWill My Dog Kill My Rabbit Are you worried about introducing your dog to your new pet rabbit? Introducing different pets to each other can be a …
Read ArticleWhat Happens If You Eat Insulation Insulation is a common material used to regulate temperature and improve energy efficiency in buildings. However, …
Read ArticleIs Canned Salmon Good For Dogs Salmon is often touted as a healthy and nutritious food for humans, but can it also benefit our canine companions? Many …
Read ArticleDog Glucosamine Overdose Are you worried about your dog’s joint health? Table Of Contents Understanding Glucosamine Recognizing Symptoms of …
Read ArticleCan A Human Outrun A Dog When it comes to speed, few animals can match the agility and quickness of a dog. Whether it’s a greyhound racing around a …
Read Article