Is The Target Dog Still Alive: Unveiling the Truth
Is The Target Dog Still Alive For years, the Target Dog has become an iconic figure in the world of advertising. With its playful demeanor and …
Read Article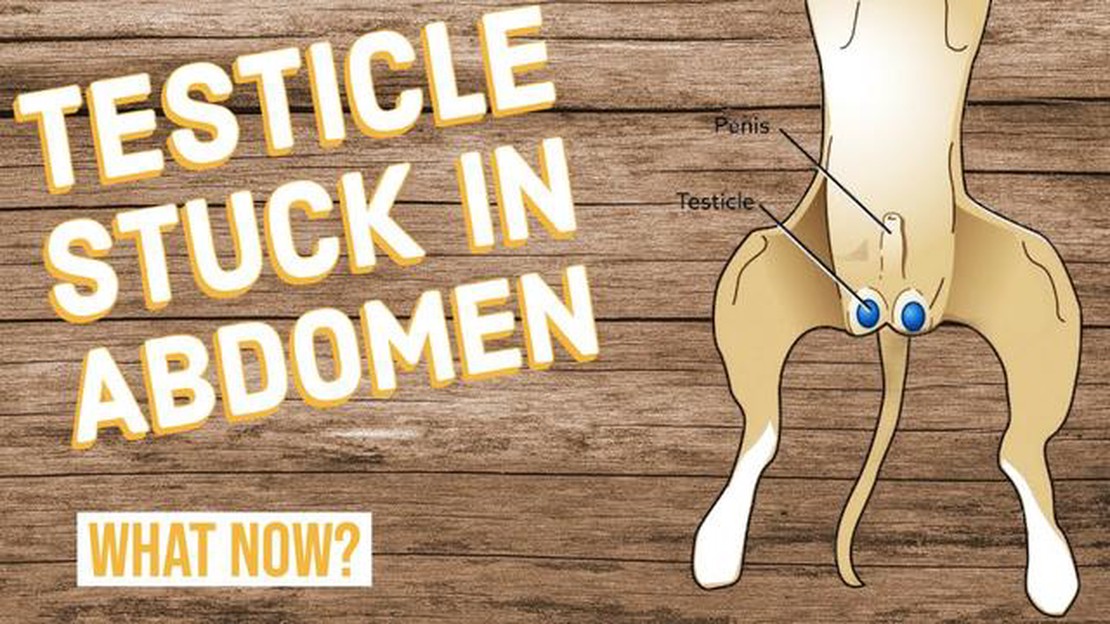
Dogs, like humans, go through various stages of development as they grow. One important aspect of a male dog’s development is the growth of their testicles. Understanding when and how this development occurs can help pet owners and breeders better care for their dogs.
In general, male dogs’ testicles start to develop at around six to eight weeks of age. This is when the testicles begin to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum. It is important to note that the exact timing may vary between individual dogs, and some dogs may experience delayed or incomplete testicular development.
During this period of testicular development, it is crucial to monitor the dog’s health and ensure they receive proper nutrition. A balanced diet with essential nutrients can support the growth and development of the testicles. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian can also help ensure that the dog’s testicles are developing normally and that there are no underlying health issues.
As the dog matures, the testicles should continue to grow and reach their full size, usually by the time the dog is six to eight months old. However, it is essential to note that each dog is unique, and some breeds may have variations in their testicular development timeline. It is always recommended to consult with a veterinarian or a reputable breeder who can provide specific information about a particular breed’s testicular development.
The development of testicles in male dogs plays a crucial role in their overall reproductive health and behavior. As the testicles begin to grow and mature, they start to produce and release important hormones such as testosterone, which directly affects a dog’s behavior, physical characteristics, and fertility.
Here are some key points to understand about the significance of testicular development in male dogs:
The primary function of testicles is to produce and release testosterone, the main male sex hormone. Testosterone is responsible for the development and maintenance of secondary sex characteristics in male dogs, such as deepening of the voice, muscle development, and the growth of facial and body hair. It also influences a dog’s behavior by contributing to territorial marking, aggression, and dominance.
The development of testicles is closely linked to a dog’s sexual maturity. Typically, when a male dog reaches the age of sexual maturity, which is around six to nine months, their testicles will have developed fully. This is often accompanied by changes in behavior and a heightened interest in female dogs.
The development of healthy testicles is essential for a male dog’s reproductive function. Testosterone production stimulates the production of sperm and is necessary for successful breeding. Dogs with underdeveloped or absent testicles may experience fertility issues, which can impact their ability to reproduce.
Regular monitoring of testicular development is an important aspect of dog health care. Early detection of abnormalities, such as undescended or incomplete testicles, can help identify potential health issues and may require medical intervention. Veterinarians often perform routine exams to ensure proper testicular development and address any concerns.
Understanding the significance of testicular development in male dogs can help dog owners recognize the importance of monitoring their pet’s reproductive health. It also highlights the need for responsible breeding practices and early intervention in case of any abnormalities.
Understanding the timing of testicular development in male dogs is important for several reasons. It can provide valuable information for dog owners and breeders, allowing them to make informed decisions about breeding, health, and behavior.
Here are some reasons why knowing when dogs’ balls grow is important:
Overall, knowing when dogs’ balls grow can enhance the welfare of male dogs and contribute to responsible breeding practices. It empowers dog owners and breeders with knowledge that can positively influence their pets’ health, behavior, and overall quality of life.
The testicular development in male dogs can be divided into four stages:
It is important to note that the exact timing of testicular development can vary between individual dogs. While the general timeline mentioned above is common, there may be individual variations. If you have concerns or questions about the development of your male dog’s testicles, it is best to consult with a veterinarian.
The embryonic stage is the first phase of testicular development in male dogs. It occurs during the early stages of the dog’s development in the womb. The testes, which are the primary male reproductive organs, begin to form during this stage.
Testicular development in male dogs starts with the differentiation of the gonads. Initially, the gonads are undifferentiated and have the potential to develop into either testes or ovaries. However, in male dogs, the presence of the Y chromosome triggers the development of testes.
At around day 30 of gestation, the cells of the gonads start to divide and form primitive sex cords. These sex cords eventually give rise to the seminiferous tubules, which are the structures responsible for producing sperm. The sex cords also contain cells called Sertoli cells, which play an important role in supporting and nourishing the developing sperm cells.
During this stage, the dog’s testes also start to produce hormones. One of the most important hormones produced by the developing testes is anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), which causes the regression of the Müllerian ducts. Müllerian ducts are the precursors to female reproductive organs, so their regression is essential for the development of the male reproductive system.
In addition to AMH, the embryonic testes also start producing testosterone. Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and plays a crucial role in the development of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, and behaviors.
Read Also: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Eliminate Coccidia In Dogs?
By the end of the embryonic stage, the testes in male dogs have developed and differentiated, and the process of testicular development continues through subsequent stages. Understanding the embryonic stage of testicular development is important for studying the overall reproductive development in male dogs.
The pubertal stage in male dogs marks the beginning of sexual maturity and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. During this stage, the testicles continue to grow and develop, reaching their full size and weight. This usually occurs around 6 to 9 months of age, but it can vary depending on the breed and individual dog.
Read Also: Are Peace Lilies Harmful to Dogs: Exploring the Dangers
As the testicles mature, they become more visible and palpable. The scrotum, which is the sac that contains the testicles, may also undergo changes during this stage. It may become looser and more pendulous, allowing for proper temperature regulation and sperm production.
During puberty, hormonal changes occur, leading to the development of male behaviors and sexual characteristics. Male dogs may start to exhibit signs of sexual interest, such as marking territory, mounting objects, or displaying aggression towards other male dogs. This is a natural part of their development and is driven by the increased levels of testosterone in their bodies.
It is important to note that even though male dogs reach sexual maturity during the pubertal stage, it does not necessarily mean they are ready for breeding. Breeding should be done responsibly and only when the dog is physically and mentally mature enough to handle the responsibilities of fatherhood.
During this stage, it is recommended to closely monitor the development of the testicles and scrotum. Any abnormalities or concerns should be brought to the attention of a veterinarian. They can provide guidance and advice on the proper care and management of a dog’s reproductive health.
In conclusion, the pubertal stage of testicular development in male dogs is an important milestone in their reproductive maturity. It is a time when the testicles grow and develop, secondary sexual characteristics emerge, and hormonal changes drive male behaviors. Responsible monitoring and veterinary care ensure the overall health and well-being of the dog during this critical stage of development.
The timing of testicular growth in male dogs is influenced by several factors. These factors can vary between individual dogs and can affect the age at which dogs’ testicles start to grow and develop.
Here are some factors that can affect the timing of dogs’ testicular growth:
It is important to note that the timing of testicular growth can vary between individual dogs, and there is no specific age at which all dogs’ testicles will start to grow. It is recommended to consult with a veterinarian for more information and guidance on the timing of testicular development in your specific dog.
The breed and size of a dog can have a significant influence on the testicular development. Different dog breeds have distinct characteristics and grow at different rates. This can affect when their testicles start to develop and when they reach maturity.
Smaller dog breeds generally have faster rates of maturation compared to larger breeds. Toy and small breeds tend to reach sexual maturity earlier, typically between 6 to 8 months of age. On the other hand, larger breeds may take longer to fully develop, with some reaching maturity between 12 to 24 months of age.
It is important to note that the size and breed of the dog are not the only factors that influence testicular development. Genetics, diet, and overall health also play a role in the timing and rate of development.
Additionally, testicular development can be influenced by factors such as neutering. Neutering male dogs at a young age can impact the growth of the testicles and delay the onset of sexual maturity. This is because neutering removes the source of hormones that promote testicular development.
In summary, the breed and size of a dog can affect the timing and rate of testicular development. Smaller breeds tend to mature earlier compared to larger breeds. However, it is important to consider other factors such as genetics, diet, and neutering when assessing testicular development in male dogs.
Male dogs’ testicles typically start to develop between the ages of 6 to 8 weeks.
It takes approximately 6 to 8 months for a male dog’s testicles to fully develop.
Some signs that a male dog’s testicles are growing include the appearance of small, firm, and symmetrical bumps in the scrotum area.
Yes, it is normal for one testicle to grow faster than the other in male dogs. It usually takes a few weeks for both testicles to become fully developed.
Yes, the size of a male dog’s testicles can vary depending on the breed. Some breeds may have larger testicles compared to others.
If your male dog’s testicles have not grown by the age of 8 months, it is recommended to consult with a veterinarian to rule out any underlying health issues.
Is The Target Dog Still Alive For years, the Target Dog has become an iconic figure in the world of advertising. With its playful demeanor and …
Read ArticleWhy Does My Dog Roll Around On The Carpet Have you ever wondered why your dog loves to roll around on the carpet? This seemingly strange behavior can …
Read ArticleDog Shows Teeth When Scolded Scolding a dog is a common part of training and discipline, but what does it mean when your furry friend shows their …
Read ArticleHow Much Onion Powder Is Toxic To Dogs Onion powder is a common ingredient in many dishes, but did you know that it can be toxic to dogs? While onions …
Read ArticleCourage The Cowardly Dog Stream Discover the fascinating and heartwarming adventures of Courage, the brave and lovable dog who faces his fears to …
Read ArticleDiabetes In Dogs Symptoms Shaking Diabetes is a common condition in dogs that affects their ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Just like humans, …
Read Article