Transitioning Your Puppy From 3 Meals to 2: A Step-by-Step Guide
How To Transition Puppy From 3 Meals To 2 As your puppy grows older, their nutritional needs may change. One of the important transitions to consider …
Read Article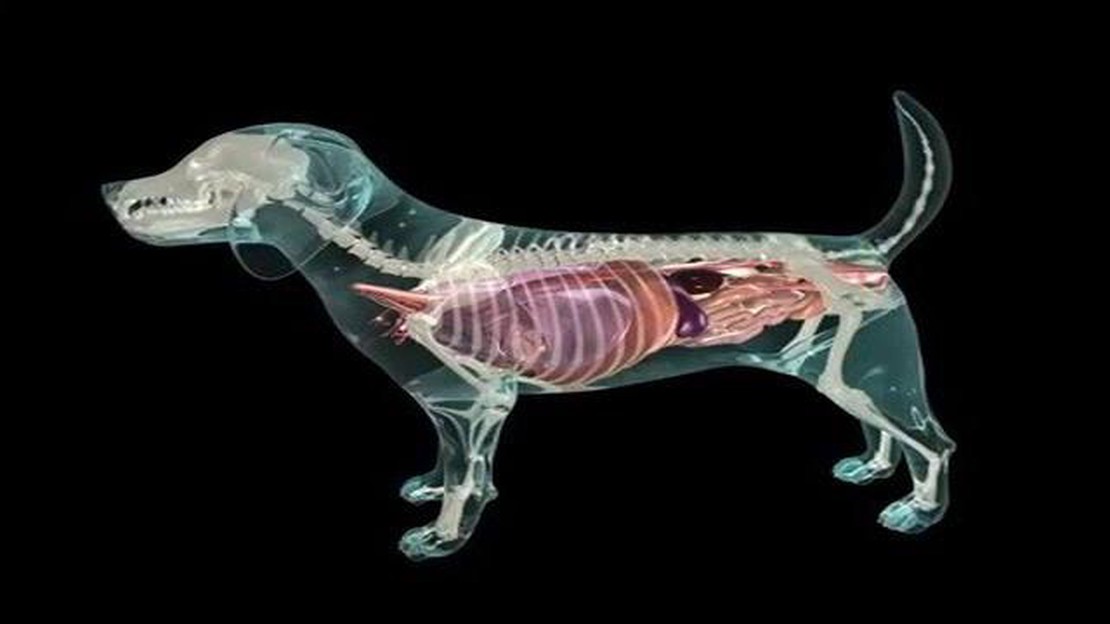
As a pet owner, it is important to have a basic understanding of your dog’s anatomy and physiology. One crucial aspect to be aware of is the location of your dog’s heart. Knowing where your dog’s heart is located can help you detect any abnormalities or potential health issues.
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. In dogs, the heart is located in the chest, just behind the front legs. It is positioned slightly to the left side of the chest, closer to the left lung.
While every dog is unique, understanding the general location of the heart can be beneficial. By familiarizing yourself with this information, you will be able to better monitor your dog’s heart health and be alert to any changes in their behavior or physical condition that may indicate a heart problem.
If you suspect any issues with your dog’s heart, it is crucial to seek veterinary care immediately. Your veterinarian can perform a thorough examination, including listening to the heart with a stethoscope and potentially ordering additional tests, such as an electrocardiogram or an ultrasound, to evaluate your dog’s heart function.
Remember, your dog’s heart plays a vital role in their overall health and well-being. By understanding its location and being proactive in monitoring your dog’s heart health, you can help ensure a happy and healthy life for your furry friend.
A dog’s heart is a vital organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Understanding its anatomy is crucial for every pet owner to ensure the well-being of their furry friend.
Size and Location: The size of a dog’s heart varies depending on the breed and size of the dog, but it is generally located in the chest behind the ribcage, between the lungs, and slightly to the left. The heart is protected by the sternum and ribcage.
Chambers: A dog’s heart consists of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria are the upper chambers that receive blood from different areas of the body, while the ventricles are the lower chambers responsible for pumping the blood out to the body.
Valves: The heart of a dog contains several valves that ensure the proper flow of blood through the chambers. The valves open and close to prevent the backflow of blood and to maintain a one-way flow.
Blood Vessels: The heart is connected to a network of blood vessels that transport oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart. The major blood vessels connected to the heart include the aorta, pulmonary artery, vena cava, and pulmonary veins.
Coronary Circulation: The heart itself also requires its own blood supply. Coronary arteries branch off from the aorta and provide oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The coronary veins then collect the deoxygenated blood and return it to the right atrium of the heart.
Electrical System: The dog’s heart has its own electrical system that controls the rhythm and rate of the heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node acts as the pacemaker, initiating the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat.
Importance of a Healthy Heart: Keeping a dog’s heart healthy is essential for their overall well-being. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine veterinary check-ups are essential for maintaining a healthy heart.
In summary, understanding the anatomy of a dog’s heart provides crucial knowledge for every pet owner. With this understanding, pet owners can better care for their furry friends and ensure their heart’s health and well-being.
As a pet owner, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of your dog’s anatomy, including the location of their heart. Knowing the location of your dog’s heart can help you to monitor their health and potentially save their life in an emergency situation.
1. Monitoring Your Dog’s Heartbeat:
By familiarizing yourself with the location of your dog’s heart, you can easily monitor their heartbeat. A strong and regular heartbeat is a sign of a healthy heart, while irregular or weak beats may indicate an underlying issue that requires veterinary attention.
2. Recognizing Symptoms of Heart Disease:
Heart disease is a common condition in dogs, and early detection is key to successful treatment. By knowing where your dog’s heart is located, you can be more aware of any symptoms that may indicate a heart problem. These symptoms may include coughing, difficulty breathing, fatigue, fainting, or a decreased appetite.
3. Administering CPR:
In an emergency situation, such as cardiac arrest, knowing the location of your dog’s heart is crucial for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). CPR can help to restore blood circulation and potentially save your dog’s life until veterinary assistance is available.
4. Communicating with Your Veterinarian:
When discussing your dog’s health with your veterinarian, knowing the location of their heart can help you to provide more accurate information. It can also aid in understanding any potential diagnostic tests or treatment options that may be recommended.
5. Preventing Accidental Injuries:
Read Also: Is Trader Joe's Peanut Butter Safe For Dogs? Find Out Here
By being aware of your dog’s heart location, you can take precautions to prevent accidental injuries. For example, knowing the location of their heart can help you properly position your hands when administering medication or performing first aid, reducing the risk of causing harm.
Summary
| Benefits of Knowing Your Dog’s Heart Location: | | - Monitor their heartbeat | | - Recognize symptoms of heart disease | | - Administer CPR in emergencies | | - Communicate effectively with your veterinarian | | - Prevent accidental injuries |
Overall, knowing the location of your dog’s heart is essential for their overall well-being. It empowers you as a pet owner to better care for their health and respond effectively in emergency situations.
Understanding the location of your dog’s heart is crucial for every pet owner. Knowing where it is can help you monitor your dog’s heart health and detect any abnormalities or issues early on. Below is a guide to help you locate your dog’s heart:
Remember, locating the dog’s heart is just the first step in understanding and monitoring your pet’s heart health. Regular veterinary check-ups and screenings are essential to ensure your dog’s overall well-being.
Read Also: Is Rotisserie Chicken Safe and Beneficial for Dogs with Diarrhea?
The heart is a vital organ in a dog’s body, playing a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to various organs and tissues. Understanding the importance of the dog’s heart and how to keep it healthy is essential for every pet owner.
Circulation:
The heart’s primary function is to circulate blood throughout the dog’s body. It pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body, supplying cells with the necessary nutrients and oxygen. At the same time, it collects deoxygenated blood, which is then sent back to the lungs to be reoxygenated.
Regulating Body Temperature:
The heart plays a role in regulating a dog’s body temperature. When a dog’s body temperature rises, the heart increases blood flow to the skin’s surface, promoting heat dissipation through panting and sweating. This helps the dog cool down and maintain a healthy body temperature.
Supporting Immune System:
The heart also has a role in supporting the immune system. It helps transport immune cells and antibodies throughout the body, allowing them to reach infection sites and fight off pathogens. A healthy heart ensures optimal immune response, keeping the dog protected from various illnesses.
Removing Waste Products:
The heart aids in removing waste products from the body. It helps circulate blood to the kidneys and liver, organs responsible for filtering and eliminating waste. By maintaining proper blood flow, the heart ensures efficient removal of toxins and waste products, promoting overall health.
Preventing Heart Disease:
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial in preventing heart disease. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine veterinary check-ups are essential to keep the heart functioning optimally. Certain breeds may be predisposed to heart conditions, making early detection and proper management even more important.
Taking Care of the Dog’s Heart:
To ensure the dog’s heart remains healthy, pet owners should prioritize a few key factors. They should provide regular exercise to keep the heart muscle strong and promote circulation. A balanced diet that is appropriate for the dog’s breed, age, and size is also crucial. Regular veterinary check-ups, including heart screenings, are essential for early detection of any potential issues.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy heart is vital for overall canine health. Understanding the role of the dog’s heart in circulation, temperature regulation, immune support, and waste removal can help pet owners take better care of their furry companions.
It’s important for pet owners to be aware of these common heart conditions in dogs and to seek veterinary care if they notice any symptoms or concerns. Regular check-ups and preventative measures, such as heartworm prevention, can help maintain a dog’s heart health and overall well-being.
Your dog’s heart health is crucial for their overall well-being. Here are some tips and recommendations to help you take care of your furry friend’s heart:
By following these tips and recommendations, you can help ensure that your dog’s heart stays healthy and strong, promoting a long and happy life for your beloved pet.
Sure! A dog’s heart is comprised of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The atria then contract, pushing the blood into the ventricles. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs to be oxygenated, while the left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Knowing the location of a dog’s heart is important for several reasons. It can help pet owners monitor their dog’s heart rate and identify any irregularities. It is also important for veterinarians to know the location in order to perform accurate physical examinations and diagnostic tests. Additionally, understanding the location can help pet owners recognize symptoms of heart disease in their dogs.
A dog’s heart is located in the chest, between the lungs. It is positioned slightly to the left side of the chest. It is important to note that the exact location may vary slightly depending on the size and breed of the dog.
To check your dog’s heart rate, you can place your hand on their chest, just behind their front leg. You should be able to feel the heartbeat. You can then count the number of beats in a certain amount of time (such as 15 seconds) and multiply it by four to get the beats per minute. Alternatively, you can use a stethoscope to listen to your dog’s heart rate.
The symptoms of heart disease in dogs can vary, but some common signs include coughing, difficulty breathing, fatigue, decreased appetite, and fainting. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Yes, certain dog breeds are more prone to heart disease. Some breeds that are known to be at a higher risk include Cavalier King Charles Spaniels, Doberman Pinschers, Boxers, and Great Danes. However, heart disease can occur in any breed, so it is important for all dog owners to be aware of the signs and symptoms.
How To Transition Puppy From 3 Meals To 2 As your puppy grows older, their nutritional needs may change. One of the important transitions to consider …
Read ArticlePuppy Regression 4 Months If you’re a puppy owner, you may have experienced the frustration of dealing with puppy regression. At around 4 months, …
Read ArticleDo Vibration Collars Work When it comes to dog training, there are numerous methods and tools available to help owners shape their dogs’ behavior. One …
Read ArticleHow Many Dog Beds Should A Dog Have When it comes to providing a comfortable and cozy spot for your furry friend, a dog bed is a must-have item. …
Read ArticleCan I Feed My Medium Dog Large Breed Food When it comes to choosing the right food for your furry friend, it’s important to consider their specific …
Read ArticleIs Rosemary Poisonous To Dogs Rosemary is a well-known herb that is often used in cooking and as a natural remedy for various ailments. However, pet …
Read Article