Dog Itching After Antibiotics: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Dog Itching After Antibiotics Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to dogs to treat a variety of bacterial infections. However, one potential side …
Read Article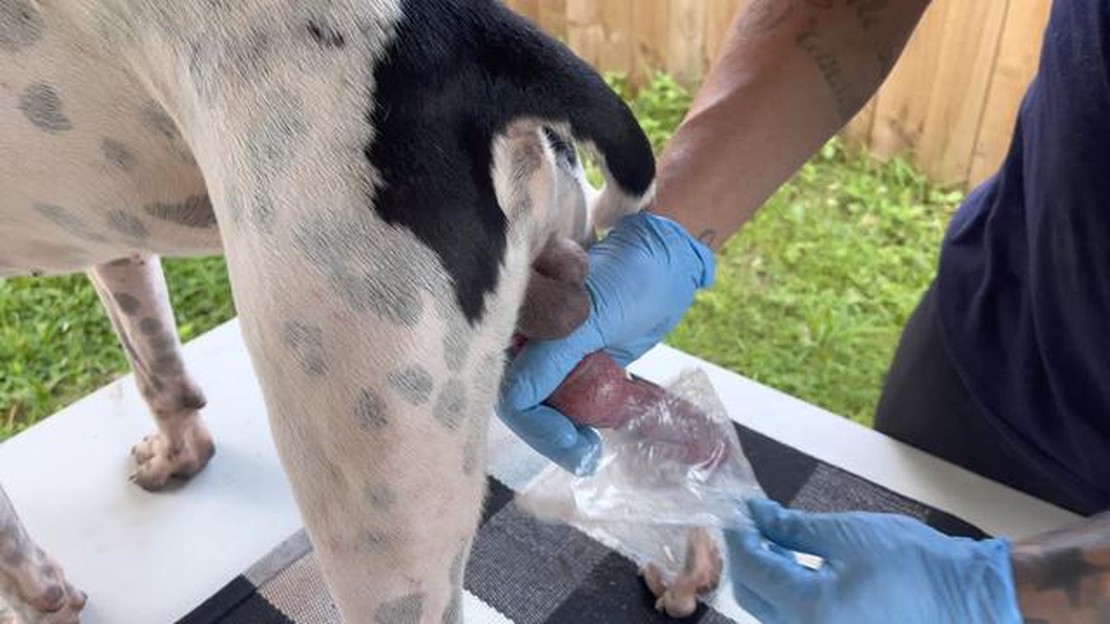
When it comes to canine reproduction, it’s natural to have questions about various aspects of the process. One specific question that often comes up is how much semen does a dog ejaculate. This is an important question for dog breeders and veterinarians alike, as the answer can provide valuable insight into a dog’s fertility and reproductive health.
Average ejaculate volume in dogs can vary depending on a range of factors, including the size and breed of the dog. On average, a dog’s ejaculation can produce around 5 to 30 milliliters of semen. This can contain anywhere from 300 million to 2 billion sperm cells. It’s important to note that not all of the ejaculate consists of sperm cells, as the semen also contains various fluids and proteins that help nourish and protect the sperm.
Understanding the amount of semen a dog produces can be useful for breeders who are trying to maximize their dog’s reproductive potential. Dogs with a larger ejaculate volume and higher sperm count are generally more fertile and have a higher chance of successfully impregnating a female. Additionally, veterinarians may use semen volume as an indicator of a male dog’s overall reproductive health.
It’s important to keep in mind that there can be variations in ejaculate volume between individual dogs within a breed or even within the same dog over time. Factors such as age, health, and stress levels can all impact a dog’s reproductive performance. If you have concerns about your dog’s fertility or reproductive health, it’s always best to consult with a veterinarian who specializes in canine reproduction.
Canine reproduction plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of the dog population. It not only ensures the continuation of specific breeds but also contributes to the diversity and adaptability of the canine gene pool. Understanding the importance of canine reproduction is essential for responsible dog owners and breeders.
Breed Preservation:
One of the primary reasons for canine reproduction is to preserve specific breeds. Breeding dogs with desirable traits helps maintain the distinct characteristics and standards of different breeds. This allows for the continuation of breeds with unique physical and behavioral attributes.
Genetic Diversity:
Canine reproduction is crucial for maintaining genetic diversity within the dog population. The more diverse the genes are, the better the dog’s ability to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases. By allowing for the mixing of genes through breeding, we can ensure that future generations of dogs have a broad genetic diversity.
Working Dogs and Service Dogs:
Reproduction is especially important for working dogs and service dogs trained for specific tasks. These dogs are selected and bred for their abilities to perform tasks such as search and rescue, therapy, or herding. Canine reproduction ensures the continued availability of dogs with the necessary physical and mental traits for these specialized jobs.
Research and Development:
Canine reproduction also plays a significant role in research and development. Studying the process of reproduction in dogs can provide valuable insights into reproductive health, fertility, and development. This knowledge can be applied to improve reproductive technologies, such as artificial insemination or genetic testing, benefiting both dogs and humans.
Companionship and Emotional Support:
Finally, canine reproduction allows for the existence of companion dogs, providing emotional support, companionship, and joy to countless individuals and families. Responsible breeding helps ensure that these dogs are healthy, well-tempered, and free from inheritable diseases, enhancing the bond between humans and dogs.
In conclusion, canine reproduction is essential for preserving specific breeds, maintaining genetic diversity, producing working and service dogs, advancing research, and providing companionship. Responsible breeding practices are crucial to ensure the health and well-being of future generations of dogs and to support the various roles they play in our society.
Dogs are fascinating creatures with unique reproductive processes. Understanding the basics of canine reproduction can offer valuable insight into their behavior and breeding patterns.
Reproductive Anatomy of Dogs
Male dogs, also known as studs, have testicles that produce sperm. These sperm are stored in the epididymis until ejaculation. The male reproductive system also includes the penis, which becomes erect during mating.
Female dogs, also known as bitches, have a reproductive system made up of the uterus, ovaries, and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs, or ova, which are released during estrus, also known as the heat cycle.
The Heat Cycle
The heat cycle is a unique aspect of canine reproduction. Bitches typically experience their first heat cycle between the ages of six months to two years, depending on the breed and size. The heat cycle consists of four phases:
Mating and Reproduction
Mating in dogs involves the male mounting the female from behind and penetrating her vagina. Ejaculation occurs, releasing sperm into the female’s reproductive tract. The fertile period during estrus typically lasts for a few days.
If successful fertilization occurs, the embryos travel to the uterus, where they implant and develop into puppies. The gestation period for dogs is approximately 63 days.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of canine reproduction can help dog owners and breeders make informed decisions about breeding and responsible pet ownership. It is essential to be aware of the heat cycle and the mating process to ensure the best possible outcomes for dogs’ reproductive health.
The volume of ejaculate produced by a dog can vary depending on several factors. These factors can include the dog’s age, breed, overall health, and reproductive experience. Here are some of the key factors that can affect the volume of a dog’s ejaculate:
It’s important to note that the volume of ejaculate does not necessarily correlate with fertility or reproductive success. Even if a dog produces a smaller volume of ejaculate, it can still be fertile and capable of successful breeding. Other factors, such as sperm count and motility, play a more significant role in determining fertility.
Read Also: Essential Paperwork to Collect When Purchasing a New Puppy
In conclusion, several factors can affect a dog’s ejaculate volume, including age, breed, health, and reproductive experience. However, ejaculate volume alone may not be an accurate indicator of fertility or reproductive success. It’s essential to consider other factors, such as sperm count and motility, when assessing a dog’s reproductive capabilities.
When it comes to measuring the ejaculate of a dog, there are a few key factors to consider. The volume, concentration, and motility are all important measurements that can provide insight into a dog’s reproductive health.
Volume: The volume of a dog’s ejaculate can vary greatly depending on the breed, size, and overall health of the dog. On average, a healthy dog can produce between 1 and 30 milliliters of ejaculate. However, it’s important to note that larger breeds tend to produce larger volumes of ejaculate compared to smaller breeds.
Concentration: The concentration of the ejaculate refers to the number of sperm cells present in a given volume of ejaculate. This measurement is important for assessing the fertility of a dog. Generally, a concentration of at least 100 million sperm per milliliter is considered normal for a dog.
Motility: The motility of the sperm refers to their ability to move and swim effectively. The higher the motility, the better chances of successful fertilization. A healthy dog should have at least 70% of sperm showing progressive motility.
These measurements are typically assessed through laboratory analysis. A semen sample is collected from the dog and then evaluated under a microscope. The sample is diluted, and measurements of volume, concentration, and motility are recorded.
Read Also: Can A Dog Starve Itself To Death: Understanding the Dangers of Refusing Food
Why Measure Dog Ejaculate?
Measuring a dog’s ejaculate is important for several reasons:
Conclusion
Measuring the ejaculate of a dog provides valuable information about their reproductive health and fertility. The volume, concentration, and motility of the sperm can all affect the dog’s ability to successfully reproduce. By evaluating these measurements, breeders and veterinarians can make informed decisions regarding breeding, as well as diagnose and treat any reproductive health issues.
Canine ejaculation is the process by which a male dog releases semen during sexual reproduction. Semen contains sperm, which are necessary for fertilization to occur. Understanding the factors that affect canine ejaculation and fertility is important for breeding and reproductive management.
Ejaculate Volume: The amount of ejaculate produced by a male dog can vary depending on factors such as age, breed, and overall health. Generally, larger breeds tend to produce a larger volume of ejaculate compared to smaller breeds. However, it is important to note that the volume of ejaculate does not necessarily correlate with fertility.
Sperm Count: The number of sperm present in the ejaculate is a crucial factor in determining fertility. A higher sperm count increases the chances of successful fertilization. However, it is important to note that even dogs with a relatively low sperm count can still be fertile.
Sperm Motility: The ability of sperm to move effectively plays a significant role in successful fertilization. Sperm that are motile have a higher chance of reaching the female’s eggs for fertilization. Sperm motility can be affected by factors such as genetic abnormalities, infections, or hormonal imbalances.
Viability: Sperm viability refers to the ability of the sperm to survive and remain viable for fertilization. The lifespan of sperm in the female reproductive tract can vary depending on numerous factors. Generally, sperm can survive for up to five days in the female reproductive tract, but this timeframe can be affected by factors such as the female’s hormonal cycle and the quality of the reproductive environment.
Ejaculation Frequency: The frequency of ejaculation can impact a dog’s fertility. If a male dog is ejaculating too frequently, the quality and quantity of sperm may be reduced. On the other hand, if a male dog is not ejaculating regularly, there may be a buildup of old or dead sperm, which can also affect fertility. It is important to strike a balance for optimal reproductive health.
Reproductive Health: A male dog’s overall reproductive health can greatly affect his fertility. Factors such as infections, hormonal imbalances, and genetic abnormalities can all impact a dog’s ability to produce healthy and viable sperm. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper care are essential for maintaining reproductive health.
Conclusion: Understanding the factors that affect canine ejaculation and fertility is crucial for successful breeding and reproductive management. By considering factors such as ejaculate volume, sperm count, motility, viability, ejaculation frequency, and overall reproductive health, breeders and dog owners can optimize the chances of successful fertilization and healthy puppies.
When it comes to maintaining the reproductive health of your canine companion, there are a few important tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you can help to ensure the overall well-being of your dog and promote a successful reproductive system.
1. Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to keep a close eye on your dog’s reproductive health. Your vet can perform examinations and screenings to detect any potential issues early on.
2. Provide a Nutritious Diet: A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for maintaining reproductive health in dogs. Make sure your dog’s diet includes high-quality proteins, essential fatty acids, and all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
3. Manage Weight: Obesity can have a negative impact on reproductive health in dogs. Help your dog maintain a healthy weight by providing regular exercise and controlling their calorie intake.
4. Avoid Overbreeding: Overbreeding can strain a dog’s reproductive system and increase the risk of complications. Give your dog adequate time to rest and recover between breeding sessions.
5. Provide Proper Housing and Environment: Ensure that your dog has a comfortable and stress-free living environment. A clean and well-maintained living space can help prevent infections and other reproductive health issues.
6. Practice Good Hygiene: Keep your dog clean and groomed to prevent the onset of infections. Regularly check for any signs of discharge or odor that may indicate an infection or other reproductive issue.
7. Avoid Exposure to Harmful Substances: Protect your dog from exposure to chemicals, toxins, and other harmful substances that could negatively affect their reproductive health. This includes avoiding contact with pesticides, cleaning products, and certain medications.
8. Consider Spaying or Neutering: If you do not plan on breeding your dog, consider spaying or neutering them. This can help prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduce the risk of certain reproductive diseases.
Remember, every dog is unique, and their individual reproductive health needs may vary. It’s always a good idea to consult with your veterinarian for personalized advice and recommendations specific to your dog’s needs.
Canine reproduction refers to the biological process of dogs reproducing and producing offspring. It involves the mating of male and female dogs, followed by fertilization and gestation.
The amount of ejaculate produced by a dog can vary depending on factors such as breed, age, and individual variation. On average, a dog can ejaculate around 5-30 milliliters of semen per ejaculation.
Semen is the fluid that is ejaculated from the male reproductive organs during ejaculation. It contains spermatozoa (sperm cells) and various other components that are necessary for fertilization of the female’s eggs.
Yes, dogs can have multiple ejaculations during one mating session. After each ejaculation, there is a refractory period, which is a period of time when the male is unable to ejaculate again. The length of the refractory period varies between dogs.
The purpose of a dog’s ejaculation is to release spermatozoa into the female’s reproductive tract for the purpose of fertilization. It is a vital step in the process of reproduction and the continuation of the species.
The size of the ejaculate does not necessarily affect fertility. What is more important is the quality and motility of the sperm cells within the ejaculate. A smaller volume of high-quality sperm can still result in successful fertilization, while a larger volume of low-quality sperm may be less likely to result in pregnancy.
Dog Itching After Antibiotics Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to dogs to treat a variety of bacterial infections. However, one potential side …
Read ArticleWhy Didn T Arya Kill The Hound Throughout the course of “Game of Thrones,” Arya Stark and Sandor Clegane, also known as The Hound, developed a complex …
Read ArticleWill Neutering Stop A Dog From Peeing In The House One of the most common issues faced by dog owners is their pets urinating in the house. This …
Read ArticleWhat Age Can Puppies Have Rawhide Rawhide chews are a popular treat for dogs of all ages, but many pet owners wonder at what age they can introduce …
Read ArticleWhat Happens If My Dog Bites The Vet Are you a pet owner who is concerned about what might happen if your dog were to bite a vet during a visit? It’s …
Read ArticleAre Socks Bad For Dogs Dogs are known for their curious nature and propensity to chew on just about anything they can get their paws on. While this …
Read Article