Are Puppy Deposits Refundable: Everything You Need to Know
Are Puppy Deposits Refundable When you decide to bring a furry friend into your life, one of the first steps is often placing a deposit with a breeder …
Read Article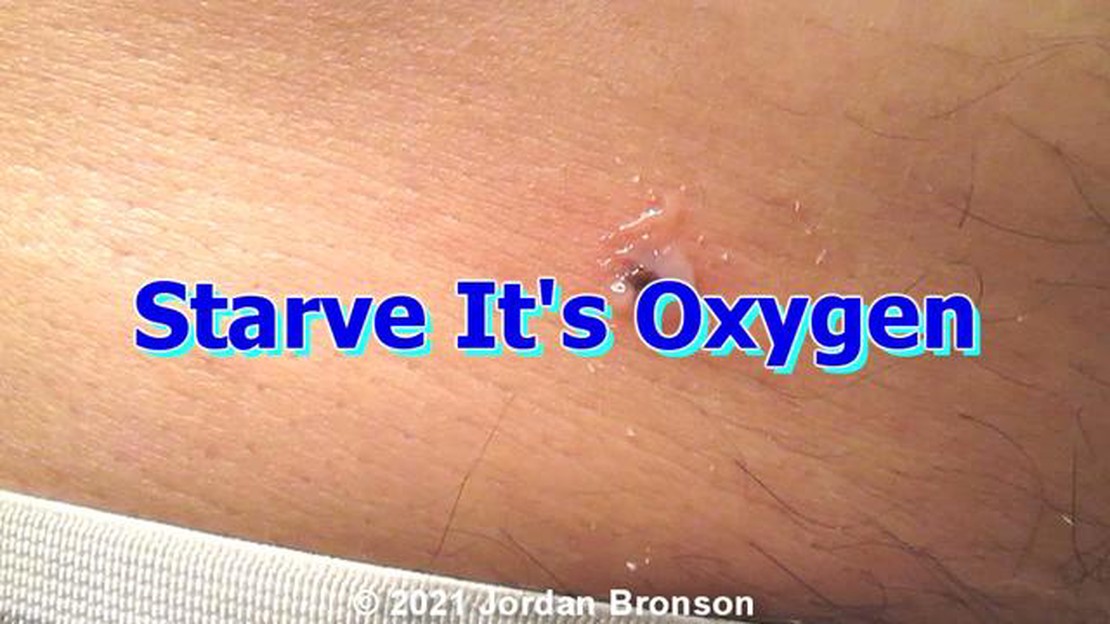
Ticks are small arachnids that feed on the blood of animals and humans. These tiny creatures are found in wooded areas, grasslands, and even in our own backyards. While they may seem harmless, ticks are known to transmit diseases such as Lyme disease, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis to both animals and humans. Understanding the importance of tick prevention and knowing how to treat tick bites is crucial in keeping ourselves and our loved ones safe.
Preventing tick bites is the first line of defense against tick-borne diseases. Wearing appropriate clothing, such as long sleeves and pants tucked into socks, can help minimize the risk of tick bites. Applying repellents containing DEET or picaridin on exposed skin can also provide protection. It is equally important to conduct thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors and to promptly remove any ticks that may have attached to the skin.
If a tick does manage to attach to the skin, it is important to remove it correctly to reduce the risk of disease transmission. Using fine-tipped tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. After the tick has been removed, clean the area with soap and water or an antiseptic. It is important to monitor the site of the tick bite for any signs of infection or illness, such as a rash or flu-like symptoms, and seek medical attention if necessary.
Tick-borne diseases can have serious consequences if left untreated. Lyme disease, for example, can cause joint pain, fatigue, and even neurological problems. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment with antibiotics are essential to prevent complications. If you develop any symptoms after being bitten by a tick, it is important to seek medical attention and inform your healthcare provider about the tick bite.
In conclusion,
ticks can be a nuisance, but their impact goes beyond just itching and irritation. Being aware of the importance of tick prevention, knowing how to properly remove ticks, and seeking prompt medical attention if necessary can help protect us from the risks associated with tick-borne diseases. So, next time you venture outdoors, take precautions to avoid ticks and enjoy nature without the worry of these tiny parasites.
Ticks are becoming an increasingly concerning issue for humans. These small arachnids, often found in grassy and wooded areas, can transmit a variety of diseases to humans through their bites.
Tick-borne diseases such as Lyme disease, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis have been on the rise in recent years. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported a significant increase in the number of tick-borne illness cases, making ticks a growing public health concern.
Preventing tick bites is crucial in minimizing the risk of contracting these diseases. Simple measures like wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants, using insect repellents containing DEET, and regularly checking for ticks after spending time outdoors can significantly reduce the chances of being bitten.
If a tick is found attached to the skin, it is important to remove it promptly and correctly to avoid any potential infections. Using fine-tipped tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with a steady, even pressure. Avoid twisting or jerking the tick, as this may cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin.
After removing the tick, it is recommended to clean the site of the bite with soap and water, as well as disinfecting the tweezers. It is also advisable to save the tick for identification purposes, in case any symptoms develop later on.
If symptoms such as fever, rash, fatigue, or muscle aches occur after a tick bite, seeking medical attention is essential. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing complications from tick-borne diseases.
Given the growing concern about ticks and the potential risks they pose to human health, it is crucial to raise awareness about prevention methods, regular tick checks, and proper tick removal techniques. Education and vigilance in high-risk areas can help in reducing the impact of tick-borne diseases on human populations.
Ticks are small, blood-sucking parasites that can transmit diseases to humans. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with ticks and take preventative measures to avoid being bitten.
Tick-borne diseases, such as Lyme disease, can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, joint pain, and muscle aches. If left untreated, these diseases can lead to more serious complications, such as neurological problems and heart conditions.
Tick bites often go unnoticed, as ticks are small and commonly attach to areas of the body that are difficult to see, such as the scalp, armpits, and groin. Therefore, it is crucial to be vigilant and regularly check for ticks after spending time in outdoor areas where ticks are prevalent.
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding tick bites. Here are some important measures to take:
If you do find a tick on your body, it is important to safely remove it as soon as possible. Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Avoid twisting or jerking the tick, as this can cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin.
Read Also: Do Poodles Have Webbed Feet: A Closer Look at this Common Canine Trait
After removing the tick, clean the bite area with soap and water or rubbing alcohol. It is also helpful to save the tick in a sealed container for identification purposes, in case you develop any symptoms and need to seek medical attention.
By being aware of the risks associated with ticks and taking necessary precautions, you can reduce the chances of being bitten and contracting a tick-borne disease. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and enjoy the outdoors safely!
Ticks can pose a threat to outdoor enthusiasts, as they can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Therefore, it is important to take precautions to prevent tick bites when spending time in nature. Here are some tips for outdoor enthusiasts:
It is crucial to practice these tick prevention tips consistently to reduce the risk of tick-borne diseases. By taking these precautions, outdoor enthusiasts can enjoy their time in nature while minimizing the chance of tick bites and the potential health risks associated with them.
Tick-borne illnesses are caused by infectious agents that are transmitted to humans through tick bites. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these illnesses in order to seek prompt medical attention and receive appropriate treatment.
Common signs of tick-borne illnesses include:
Read Also: Heartbreaking: Puppy Dies After Bath - Find Out the Possible Causes and How to Prevent It
In addition to these common signs, tick-borne illnesses can also lead to more severe symptoms, depending on the specific infection and individual response. These may include:
If you have been bitten by a tick and experience any of these signs or symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice. Early detection and treatment can help prevent further complications and promote a faster recovery.
Please remember to take preventive measures when spending time in tick-infested areas, such as wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and checking for ticks on yourself, your family members, and your pets.
Tick bites can potentially transmit various diseases to humans. Therefore, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you have been bitten by a tick. Proper treatments can help prevent the development of tick-borne illnesses.
1. Tick Bite Removal:
2. Tick-Borne Disease Prevention:
3. Antibiotics:
| Tick-Borne Disease | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Lyme Disease | Oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime axetil, for several weeks. |
| Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever | Immediate treatment with doxycycline to prevent severe complications. |
| Ehrlichiosis | Antibiotics, such as doxycycline, for several days to weeks depending on the severity. |
4. Other Medications:
5. Consult a Healthcare Provider:
Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to tick-borne diseases. Take necessary precautions, promptly remove ticks, and seek medical attention if needed to ensure your well-being.
Ticks are small arachnids that belong to the order Parasitiformes. There are different species of ticks, but they all have a flattened, oval-shaped body with eight legs.
When ticks feed, they use their specialized mouthparts to attach to the skin and suck blood. During this process, they may burrow their mouthparts into the skin, which makes it seem like they are “under” the skin.
Yes, ticks can be dangerous because they can transmit diseases to humans. Some common diseases transmitted by ticks include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and tick-borne encephalitis.
Ticks can be prevented by avoiding wooded and grassy areas, wearing long sleeves and pants, using insect repellent, and doing thorough tick checks after being outdoors.
If you find a tick on your body, it is important to remove it carefully. Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. After removing the tick, clean the bite area with rubbing alcohol or soap and water.
Are Puppy Deposits Refundable When you decide to bring a furry friend into your life, one of the first steps is often placing a deposit with a breeder …
Read ArticleDog Tv Of The Year Are you looking for television programming that will entertain and engage your furry friend? Look no further than Dog TV, the …
Read ArticleRubbing Coconut Oil On Dogs Gums Did you know that coconut oil can have amazing benefits for your dog’s oral health? While we all know that coconut …
Read ArticleGreen Mark On Dog Belly If you’re a dog owner, you might have noticed a mysterious green mark on your furry friend’s belly. While it may seem odd at …
Read ArticleDo Dogs Know When They Are Being Put Down One of the most difficult decisions a pet owner may face is whether or not to euthanize their dog. It is a …
Read ArticleGreen Beans For Dogs With Diarrhea Dogs are beloved family members, and it can be distressing when they experience health issues, such as diarrhea. …
Read Article