The Bull Terrier Trance: Understanding and Managing this Unique Behavior
Bull Terrier Trance Are you a proud owner of a Bull Terrier? If so, you may have witnessed a peculiar behavior known as the Bull Terrier Trance. This …
Read Article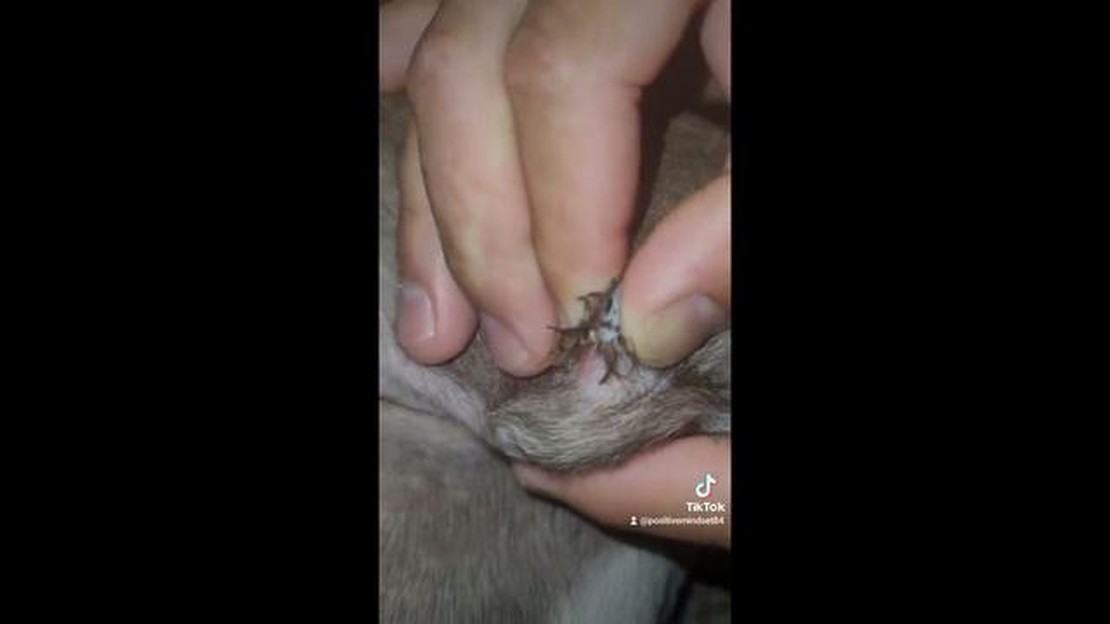
Is your furry friend suffering from an ingrown dog whisker? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered!
An ingrown dog whisker can be uncomfortable and even painful for your beloved pet. It occurs when a whisker curls back and grows into the skin instead of outward. Luckily, with proper care and treatment, you can help your dog find relief.
Causes of Ingrown Whiskers:
1. Trauma or injury to the whisker follicle.
2. Infection or inflammation.
3. Improper grooming or trimming techniques.
Symptoms to Look Out for:
1. Redness and swelling around the whisker.
2. Itching or discomfort.
3. Pus or discharge.
4. Your dog scratching or rubbing their face more than usual.
Treatment Options:
1. Gentle cleaning with warm water and mild soap.
2. Applying an antiseptic ointment to reduce inflammation.
3. If necessary, trimming the ingrown whisker carefully using clean, sterilized scissors.
4. Regular grooming to prevent future ingrown whiskers.
Remember, it’s always best to consult with a veterinarian if you are unsure or if your dog’s condition worsens. Our furry friends deserve the best care possible, and their comfort is our top priority!
An ingrown dog whisker occurs when a dog’s whisker becomes curved or embedded in the skin instead of growing straight out. This can cause discomfort and irritation for your furry friend. Ingrown dog whiskers are most commonly seen on the muzzle and around the eyes.
Causes of Ingrown Dog Whisker:
Symptoms of Ingrown Dog Whisker:
Treating Ingrown Dog Whisker:
Read Also: Dogs Can Safely Enjoy Pork Rinds: Expert Advice
In conclusion, an ingrown dog whisker can be a source of discomfort for your furry companion, but with proper care and attention, it can be treated effectively. Remember to always consult with your veterinarian if you are unsure or if the symptoms worsen. Your dog’s well-being is important, and maintaining healthy whiskers is part of their overall health and happiness.
Ingrown dog whiskers can occur due to various factors. Understanding the causes can help pet owners in preventing and treating this condition.
1. Genetic Predisposition:
Some dog breeds are more prone to ingrown whiskers compared to others. Breeds with long or curly hair, such as Poodles or Schnauzers, are more susceptible to this condition. If you have a dog of one of these breeds, it is important to be aware of the potential for ingrown whiskers.
Read Also: Why Are My Dog's Balls Sideways? Possible Causes and Solutions
2. Improper Grooming:
Poor grooming practices can contribute to the occurrence of ingrown dog whiskers. When cutting or grooming your dog’s hair, it is important to use proper techniques and tools. Trimming the whiskers too short or using dull scissors can cause them to become ingrown.
3. Skin Infections:
Underlying skin infections can also lead to ingrown whiskers. Bacterial or fungal infections can cause inflammation and blockage of the hair follicles, resulting in ingrown whiskers. Regularly checking your dog’s skin for any signs of infection and promptly treating them can help prevent ingrown whiskers.
4. Trauma or Injury:
Skin trauma or injuries can cause the whiskers to become ingrown. This can occur due to scratching, bites, or accidents. It is important to closely examine your dog’s skin and whiskers after any injury to ensure they are not becoming ingrown.
5. Poor Diet:
A poor diet lacking essential nutrients can affect the overall health of your dog’s skin and hair. When the hair follicles are weak, they are more prone to becoming ingrown. Providing your dog with a balanced and nutritious diet can help prevent this condition.
In conclusion, understanding the causes of ingrown dog whiskers is crucial for prevention and treatment. By being aware of these factors and taking appropriate measures, you can ensure that your dog’s whiskers stay healthy and free from ingrown hairs.
Ingrown dog whiskers can cause discomfort and pain for your furry friend. It is important to be aware of the symptoms so that you can provide the necessary care and treatment. Here are some common symptoms of ingrown dog whiskers:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with your veterinarian. They can properly diagnose the cause of the symptoms and provide appropriate treatment. Remember, early intervention can help prevent further complications and discomfort for your beloved pet.
An ingrown dog whisker can cause discomfort and irritation for your furry friend. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious problems. Here are some tips on how to treat ingrown dog whiskers:
Remember, it’s important to treat ingrown dog whiskers promptly to prevent any complications. If you’re unsure or concerned about treating ingrown whiskers at home, consult your veterinarian for professional guidance and treatment.
Preventing ingrown dog whiskers is essential for maintaining your pet’s health and comfort. Here are some tips to help prevent ingrown whiskers:
By following these preventative measures, you can help keep your dog’s whiskers healthy and reduce the risk of ingrown whiskers.
An ingrown dog whisker occurs when a dog’s whisker grows into the skin instead of outward. This can happen due to various reasons such as improper grooming or skin infections.
There can be several causes of ingrown dog whiskers. Some common causes include improper grooming, skin infections, trauma to the whisker follicles, or certain medical conditions that affect hair growth. It’s best to consult a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause.
The symptoms of ingrown dog whiskers may vary. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and inflammation around the affected whisker. The dog may also exhibit signs of discomfort or irritation in the affected area. If you notice any unusual symptoms, it is recommended to seek veterinary advice.
The treatment for ingrown dog whiskers depends on the severity and underlying cause. In mild cases, simply trimming the whisker carefully with clean scissors may be sufficient. However, if the ingrown whisker is causing significant discomfort or there are signs of infection, it is important to consult a veterinarian. They may recommend antibacterial ointments, oral medications, or other treatments to alleviate the condition.
In some cases, ingrown dog whiskers can lead to complications if left untreated. These complications may include skin infections, abscess formation, or inflammation. It is important to monitor the condition closely and seek veterinary advice if there are any signs of worsening symptoms or if the dog is in significant discomfort.
Bull Terrier Trance Are you a proud owner of a Bull Terrier? If so, you may have witnessed a peculiar behavior known as the Bull Terrier Trance. This …
Read ArticleHome Remedies For A Poisoned Dog If you suspect that your beloved furry friend may have been poisoned, it is important to act quickly and seek …
Read ArticleRaw Eggs For Dogs Itchy Skin If you have a dog with itchy skin, you may have heard that feeding them raw eggs can offer some relief. But is there any …
Read ArticleHow To Remove Dingleberries From Dog Dealing with dingleberries can be an unpleasant experience for both you and your furry friend. These irritating …
Read ArticleCan You File Dog Nails Human Nail File Grooming your dog’s nails is an essential part of their overall health and well-being. But what do you do when …
Read ArticleCoconut Water For Dogs Give your furry friend a refreshing and nutritious treat with coconut water! Table Of Contents The Benefits of Coconut Water …
Read Article