Can Dogs Eat Freshpet Cat Food? Everything You Need to Know
Can Dogs Eat Freshpet Cat Food As a pet owner, it’s important to provide the best nutrition for your furry friend. However, sometimes situations arise …
Read Article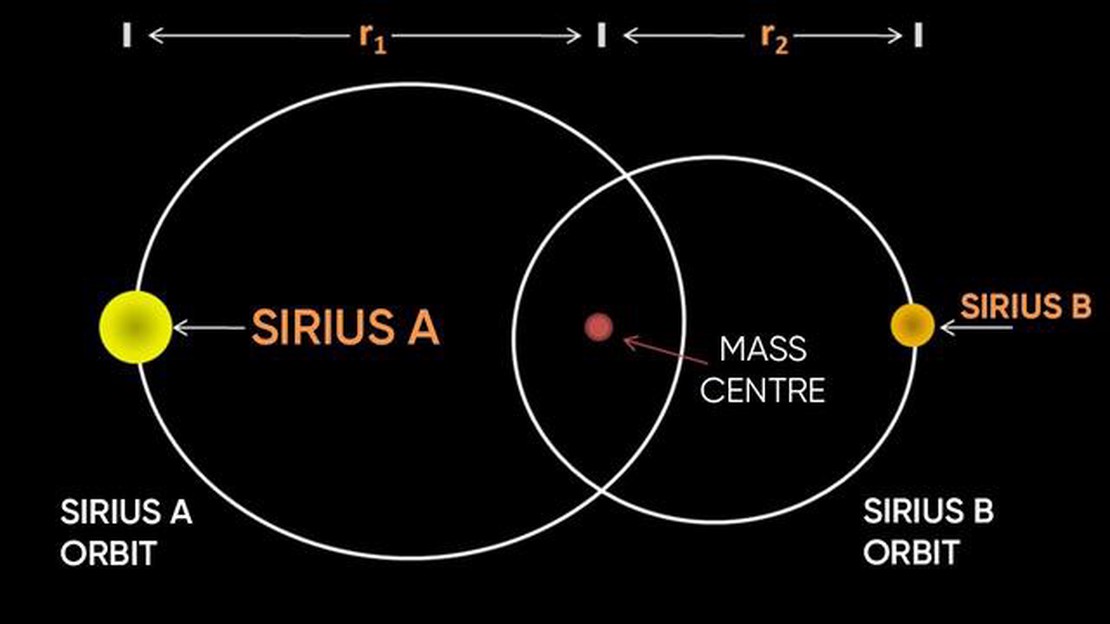
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered just how far away the stars are? One star that has captivated the human imagination for centuries is Sirius, also known as the Dog Star. As the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius has been the subject of countless myths, legends, and scientific studies. In this guide, we will explore the fascinating world of Sirius and delve into the question of just how far away it is.
To begin, let’s talk about what we know about Sirius. It is part of a binary star system, meaning that it is actually two stars orbiting around a common center of mass. The primary star, Sirius A, is the larger and more massive of the two, while the secondary star, Sirius B, is a white dwarf. Despite its smaller size, Sirius B is actually more dense than any other known star. Together, these two stars create a mesmerizing spectacle in the night sky.
So, how far away is Sirius? The answer is approximately 8.6 light-years. To put that into context, a light-year is the distance that light travels in one year, which is about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers). This means that the light we see from Sirius tonight actually left the star 8.6 years ago and has been traveling through space ever since. It’s mind-boggling to think about just how vast our universe is, and the distances we are talking about here are truly astronomical.
“We are but specks of dust in the vastness of the cosmos, looking up at the stars and wondering about our place in the universe.”- Anonymous
Studying the distance to stars like Sirius is no easy feat. Scientists use a variety of methods to calculate these distances, including parallax measurements, spectroscopic analyses, and even astrometric measurements using spacecraft. Each method has its own limitations and challenges, but through the combined efforts of astronomers around the world, we have been able to gain a better understanding of our place in the universe.
So, the next time you find yourself gazing up at the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the immense distances between the stars. Sirius, with its incredible brightness, serves as a constant reminder of just how small we are in the grand scheme of things. Yet, it also reminds us of the boundless possibilities that lie beyond our own little corner of the universe.
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky and is located in the constellation Canis Major. With an apparent magnitude of -1.46, Sirius is known for its brilliant and steady white light that makes it easily recognizable.
Sirius is a binary star system, meaning it is made up of two stars orbiting around a common center of mass. The larger and brighter star, known as Sirius A or Alpha Canis Majoris, is a main-sequence star approximately twice as massive as the Sun. It is also one of the closest stars to Earth at a distance of about 8.6 light-years.
The companion star, Sirius B or Alpha Canis Majoris B, is a white dwarf and is much smaller and fainter compared to Sirius A. Sirius B is about the size of the Earth but has a mass that is roughly equal to that of the Sun. The two stars orbit each other with a period of about 50.1 years.
Sirius has been known and observed by various ancient civilizations, including the ancient Egyptians, who celebrated its heliacal rising (its first appearance before sunrise) as a marker of the annual flooding of the Nile River.
Today, Sirius remains a popular target for amateur astronomers due to its brightness and visibility throughout the year. Its close proximity to Earth also makes it an excellent subject for scientific research, such as studying binary star systems and stellar evolution.
The brightness of stars is measured on a logarithmic scale known as the magnitude system. Astronomers use this system to classify the brightness of stars based on their apparent magnitude, which is how bright they appear to an observer on Earth.
The magnitude system was established by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus in the 2nd century BC. The original system had six magnitudes, with the brightest stars assigned a magnitude of 1 and the faintest stars assigned a magnitude of 6. Nowadays, the magnitude system has been expanded to include even fainter objects, with the brightest stars having negative magnitudes.
A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a 100-fold difference in brightness. For example, a star with a magnitude of 1 is 100 times brighter than a star with a magnitude of 6. The brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, has an apparent magnitude of -1.46, making it nearly 25 times brighter than the next brightest star, Canopus, which has a magnitude of -0.72.
It’s important to note that apparent magnitude does not actually measure the intrinsic brightness of a star. Instead, it measures how bright the star appears from Earth. To determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, astronomers use the absolute magnitude, which is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were located at a standard distance of 10 parsecs (about 32.6 light-years) from Earth.
Read Also: Understanding the Side Effects of Forbidding Certain Foods for Dogs
Table 1:
Stars are not the only celestial objects that can be measured in terms of brightness. Galaxies, nebulae, and other astronomical objects also have their own magnitudes, allowing astronomers to compare their brightness levels.
In conclusion, the astronomical brightness of stars is measured using the magnitude system. This system allows astronomers to classify the brightness of stars based on their apparent magnitude or how bright they appear from Earth. It’s important to remember that apparent magnitude does not measure the true brightness of a star, but rather how bright it appears to us. Absolute magnitude is used to measure the intrinsic brightness of a star at a standardized distance.
The distance to Sirius can be determined using various methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. Astronomers have developed several techniques to measure astronomical distances, known as stellar parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and photometric parallax.
The distance to Sirius has been measured using all of these methods, providing consistent results. It is estimated to be approximately 8.6 light-years away, making it one of the closest visible stars to Earth.
Methods for Measuring the Distance to Sirius
Read Also: What to Do If Your Dog Ate Raw Ground Beef - Essential Tips and Advice
| Method | Advantages | Limitations | | Stellar Parallax | Accurate for nearby stars | Limited to relatively close stars | | Spectroscopic Parallax | Suitable for distant stars | Dependent on stellar models | | Photometric Parallax | Reliable for stars of different distances | Requires accurate brightness and color measurements |
Sirius, also known as the Dog Star, is the brightest star in the night sky. It is located in the constellation Canis Major, and has been a prominent celestial object for centuries. But just how far is Sirius from Earth?
The distance to Sirius is approximately 8.6 light-years. This means that the light we see from Sirius today actually left the star around 8.6 years ago. In other words, when we look at Sirius, we are seeing it as it appeared over 8 years ago.
To put this distance into perspective, let’s consider how long it would take to travel to Sirius. If we were to travel at the speed of light, which is about 299,792 kilometers per second, it would take us about 8.6 years to reach Sirius. However, with our current technology, it would take us much longer to make such a journey.
The exact distance to Sirius has been measured using various astronomical techniques, including parallax and spectroscopy. These methods allow astronomers to calculate the distance to stars by measuring their apparent motion or analyzing their light spectra.
It is worth noting that Sirius is not a single star, but rather a binary star system. Sirius A is the brighter and larger star, while Sirius B is a smaller and fainter white dwarf companion. The distance between these two stars is about 20 astronomical units (AU), where 1 AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun.
In conclusion, Sirius is located approximately 8.6 light-years away from Earth. It is a binary star system and has been a fascinating object of study for astronomers throughout history.
Yes, Sirius is indeed the brightest star in the sky. It is over 20 times brighter than our Sun and can easily be seen from Earth.
Sirius is located at a distance of about 8.6 light-years from Earth.
The distance of Sirius from Earth is approximately 81 trillion kilometers.
Traveling at the speed of light, it would take about 8.6 years to reach Sirius. However, with current technology, it would take thousands of years to reach Sirius.
Yes, Sirius can be seen with the naked eye. It is one of the most easily recognizable stars in the night sky.
Sirius is also known as Alpha Canis Majoris or the Dog Star.
Can Dogs Eat Freshpet Cat Food As a pet owner, it’s important to provide the best nutrition for your furry friend. However, sometimes situations arise …
Read ArticleWill Instant Potato Flakes Hurt Dogs When it comes to feeding our furry friends, it’s important to be cautious and educated about what we give them. …
Read ArticleLoose Puppy Stool When you bring home a new puppy, it’s important to be prepared for all aspects of their care, including their digestion. One common …
Read ArticlePurina Dog Chow Vs Purina One Choosing the right dog food can be a challenging task for pet owners. With so many options available on the market, it …
Read ArticleCan Dogs Have Salsa Many pet owners love to share food with their furry friends, but it’s important to know which foods are safe for dogs and which …
Read ArticleDog Acting Different Weeks After Surgery Undergoing surgery can be a stressful experience for dogs, and it’s not uncommon for their behavior to change …
Read Article