Discover the Exo Dogs: The Future of Canine Robotics
Exo Dogs Introducing Exo Dogs: a groundbreaking innovation that merges the loyalty and intelligence of dogs with the cutting-edge technology of …
Read Article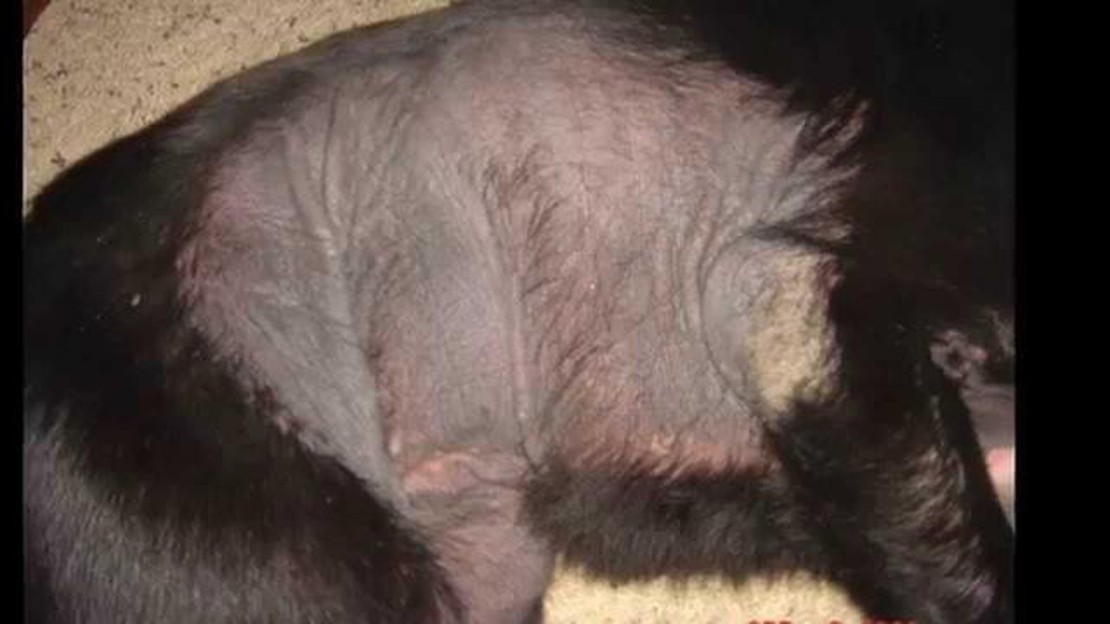
Have you ever wondered what the true color of a dog’s skin is? It’s a question that has puzzled scientists and dog lovers alike for centuries. But now, thanks to a fascinating investigation, we may finally have an answer.
The conventional belief has always been that a dog’s skin is simply a shade of pink, similar to that of humans. However, recent research suggests that this may not be the case. Scientists have discovered that the color of a dog’s skin actually varies depending on their breed and coat color.
One of the most surprising findings of the investigation is that some dogs, particularly those with lighter coats, can have skin that is almost transparent. This means that the color we see on their fur is actually a reflection of the underlying skin color. For example, a white dog with pink skin will appear to have white fur, while a black dog with pink skin will appear to have black fur.
But what about dogs with dark coats, you might ask? This is where things get really interesting. It turns out that these dogs have skin that is not pink, but rather a shade of black or gray. You may have noticed this if you’ve ever seen a dog with a bald patch – their skin will be a similar color to their fur.
So why does the color of a dog’s skin matter? Well, it’s not just a matter of curiosity. Understanding the true color of a dog’s skin can help veterinarians diagnose and treat certain skin conditions more effectively. It can also help dog groomers and breeders better understand the specific needs and characteristics of different breeds.
All in all, this investigation has opened up a whole new world of possibilities when it comes to understanding our furry friends. It just goes to show that there is still so much we have yet to discover about the animals we share our lives with.
Dog skin color plays an important role in their overall health and well-being. It is not just a cosmetic feature but can also have significant implications for their overall health and susceptibility to certain diseases.
1. Sun Protection: Just like humans, dogs can also suffer from sunburns and skin damage caused by the harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun. Dogs with lighter skin and hair are more prone to sunburns and are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
2. Heat Regulation: The color of a dog’s skin can also affect its ability to regulate body temperature. Darker-skinned dogs have a higher concentration of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin absorbs and scatters UV radiation, protecting the underlying tissues from damage. It also helps in dissipating heat more efficiently during hot weather.
3. Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as allergies, infections, and autoimmune diseases, can cause changes in a dog’s skin color. Monitoring the skin color can help detect these underlying health issues early on and seek appropriate treatment before they escalate.
4. Breed Identification: The color of a dog’s skin can also provide important clues about its breed. Different breeds have distinct skin colors and patterns, which can be indicative of their lineage and heritage. Skin color can also play a role in breed-specific health concerns and genetic predispositions.
5. Visual Appeal: Last but not least, the color of a dog’s skin can contribute to its overall visual appeal. Just like any other feature, skin color can enhance the aesthetics of a dog’s appearance, making it more attractive and desirable to potential owners or breeders.
In conclusion, dog skin color is not just a superficial characteristic but an important aspect of their health, well-being, and breed identification. It is crucial for dog owners and breeders to understand and appreciate the significance of dog skin color in order to ensure the overall health and happiness of their beloved pets.
One of the key factors that determine the color of dog skin is melanin. Melanin is a pigment responsible for the color of hair, skin, and eyes in humans and animals. In dogs, melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes.
There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for darker colors, such as black or brown, while pheomelanin is responsible for lighter colors, such as yellow or red. The ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin determines the overall color of the dog’s skin.
The production of melanin is regulated by various factors, including genetics, hormones, and environmental stimuli. Genetic factors play a significant role in determining the amount and type of melanin produced by an individual dog. Different breeds and individual dogs within the same breed can have variations in the production of melanin, resulting in a wide range of skin colors.
Furthermore, hormones can also influence melanin production. For example, during pregnancy, female dogs may experience hormonal changes that can affect the pigmentation of their skin. This can result in temporary changes in skin color, such as darkening or lightening.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can also affect melanin production. Dogs with lighter skin are more sensitive to UV radiation and may be at a higher risk of sunburn and skin cancer. On the other hand, dogs with darker skin have a higher natural protection against UV radiation due to the increased production of melanin.
Melanin Production and Skin Color
| Type of Melanin | Color | Skin Color | | Eumelanin | Black or Brown | Dark skin | | Pheomelanin | Yellow or Red | Light skin | | Eumelanin and Pheomelanin | Mixed | Variations in skin color |
In conclusion, melanin plays a vital role in determining the color of dog skin. The ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin, influenced by genetics, hormones, and environmental factors, determines the overall skin color of a dog. Understanding the role of melanin can help us appreciate the diversity of skin colors in dogs and their unique adaptations to different environments.
When it comes to understanding the true color of a dog’s skin, genetic factors play a significant role. There are several genes that contribute to the pigmentation of a dog’s skin, and the combination of these genes determines the final color.
Eumelanin and pheomelanin: Two types of pigments, eumelanin and pheomelanin, are responsible for the different colors seen in dog skin. Eumelanin is responsible for black and brown colors, while pheomelanin produces red and yellow colors.
MC1R gene: One of the key genes involved in pigmentation is MC1R. Variations in this gene can affect the production of eumelanin and pheomelanin. For example, a mutation in MC1R can result in a dog with a black coat but with a genetically brown or red skin.
Dominant black gene: Another important gene is the dominant black gene, which is responsible for the presence of black pigment. When a dog inherits two copies of this gene, it will have a black coat and black skin. However, if the dog inherits only one copy, it may have a black coat but genetically brown or red skin.
Dilution gene: The dilution gene is responsible for lightening the color of both the coat and the skin. When this gene is present, it can result in a dog with diluted colors, such as blue or fawn. In these cases, the skin color will also be affected and may appear lighter than expected.
Other genes: There are also other genes that can influence the color of a dog’s skin, such as the Agouti gene, which regulates the distribution of eumelanin and pheomelanin, and the SLC45A2 gene, which is associated with lighter skin color.
Interactions between genes: The combination and interactions of these genes can result in a wide range of skin colors in dogs. It is not uncommon to find dogs with different-colored skin patches or patterns, which can be explained by the complex interplay between these genetic factors.
Further research: The field of canine genetics is still being explored, and researchers are continuously uncovering new information about the genetic factors that influence a dog’s skin color. Understanding the genetic basis of skin pigmentation can help breeders and veterinarians better predict and manage certain skin conditions and diseases.
In conclusion, the color of a dog’s skin is determined by a combination of genes that regulate the production and distribution of pigments. Exploring these genetic factors can provide valuable insights into the fascinating world of dog coat and skin coloration.
While genetics play a significant role in determining the skin color of dogs, environmental factors also contribute to the final appearance of their skin. These influences can result in variations and changes in the coloration of dog skin.
1. Sun Exposure: The amount of sun exposure a dog receives can affect the pigmentation of its skin. Just like humans, dogs can develop a tan when exposed to the sun. Over time, increased sun exposure can darken a dog’s skin color. On the other hand, limited sun exposure can cause the skin to lighten.
2. Seasonal Changes: Dogs, particularly those with lighter skin, may experience seasonal changes in their skin color. During the summer months, their skin may darken due to sun exposure. In colder months, the lack of sunlight can cause the skin to lighten.
Read Also: Can Dogs Eat Applesauce? Everything You Need to Know
3. Nutritional Factors: Diet plays a crucial role in a dog’s overall health, including the condition of its skin. Nutritional deficiencies or imbalances can impact the skin’s pigmentation. A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals can help maintain a healthy skin color.
4. Inflammation and Irritation: Skin inflammation and irritations, such as allergies or infections, can affect the coloration of a dog’s skin. These conditions can lead to redness, blotchiness, or darkening of the affected areas.
5. Aging: As dogs age, their skin undergoes natural changes, including alterations in skin color. Just as wrinkles and gray hair appear, changes in skin pigmentation can occur as well.
6. Medications and Treatments: Certain medications or treatments, such as topical creams or ointments, can cause temporary changes in a dog’s skin color. These changes usually reverse once the treatment is discontinued.
Read Also: Discover The Decomposition Time of Dog Poop and Environmentally Friendly Solutions
7. Environmental Toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pollution or chemicals, can also impact a dog’s skin color. Harmful substances can cause discoloration or damage to the skin cells, affecting their pigmentation.
8. Stress and Emotions: Just like humans, dogs can experience stress and emotions that may affect their skin. Stress-related conditions, such as alopecia or dermatitis, can potentially alter the color of a dog’s skin.
9. Underlying Health Issues: Various health conditions, such as hormonal imbalances or liver disease, can manifest through changes in the coloration of a dog’s skin. It is essential to consult a veterinarian if any unusual skin color changes or abnormalities are observed.
In conclusion, the true color of a dog’s skin is influenced not only by genetics but also by environmental factors. Sun exposure, seasonal changes, diet, inflammation, aging, medications, environmental toxins, stress, and underlying health issues can all contribute to the variations in dog skin coloration.
Understanding the color of a dog’s skin can provide valuable insights into their overall health and well-being. The condition of a dog’s skin is closely linked to their internal health, making it an important factor to consider when assessing their overall wellness.
Skin Color and Blood Flow
The color of a dog’s skin is determined by the amount of melanin present. Melanin is a pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes. Darker skin tones are typically associated with higher amounts of melanin, while lighter skin tones indicate lower melanin levels.
Blood flow also plays a role in skin color. When the blood vessels near the surface of the skin dilate, the skin may appear ruddy or reddish. Contrarily, constricted blood vessels can result in a pale or bluish-tone skin. Monitoring a dog’s skin color can help determine if there are any issues with blood circulation.
Indicators of Health
A dog’s skin color can provide clues about their overall health. For example, a healthy dog usually has pink or light-colored skin, indicating good blood circulation and oxygenation. If a dog’s skin appears pale or bluish, it could be a sign of poor blood flow or a respiratory problem.
The presence of abnormal or discolored skin can also point to underlying health issues. Yellowish or jaundiced skin may indicate liver problems or an issue with the bile duct, while red or inflamed skin can be a sign of allergies or skin infections.
It’s crucial to regularly check a dog’s skin color and observe any changes or abnormalities. Being aware of what is normal for a dog’s skin tone can help detect potential health issues in their early stages and allow for prompt veterinary intervention.
Monitoring and Care
Regular grooming and flea prevention can contribute to healthier skin in dogs. A clean coat and skin are less prone to irritations and infections. It’s also important to ensure that dogs receive a balanced diet and proper hydration, as proper nutrition and hydration can support overall skin health.
If a dog’s skin color appears abnormal or there are concerns about their health, it’s recommended to consult a veterinarian. They can conduct a thorough examination, perform necessary tests, and provide appropriate treatment if needed. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for maintaining a dog’s health and well-being.
Understanding the connection between a dog’s skin color and their health is crucial for responsible pet owners. By regularly monitoring their dog’s skin, observing any changes, and seeking veterinary care when necessary, owners can take proactive steps to ensure their dog’s overall well-being.
The discovery of the true color of dog skin has significant implications for dog breeding and selection. It challenges the conventional notion that a dog’s coat color is solely determined by the color of its hair. Understanding the underlying pigmentation of a dog’s skin can revolutionize the way breeders select and breed dogs for desired coat colors.
Diversification of Coat Colors:
The knowledge of the true color of dog skin opens up new possibilities for diversifying coat colors. Breeders can now have a better understanding of the pigmentation patterns and can selectively breed dogs with unique coat colors. This discovery can lead to the creation of new and exciting coat color variations that were previously unknown or considered impossible.
Health Implications:
This discovery may also have health implications for certain breeds. Some coat colors have been associated with a higher risk of certain genetic disorders or health conditions. By understanding the pigmentation mechanisms in dog skin, breeders can avoid breeding dogs with potentially detrimental coat colors and reduce the risk of certain health issues in specific breeds.
Standardization and Preservation of Coat Colors:
Knowing the true color of dog skin can also help in standardizing and preserving coat colors within specific breeds. Breeders can use this information to ensure that the desired coat color is maintained and not diluted or altered due to misunderstanding or misrepresentation. This can be particularly important for breeds with unique coat colors that are highly valued or recognized by breed standards.
Identification and Authentication:
The ability to accurately determine a dog’s true skin color can also be useful for identification and authentication purposes. This information can help in situations where the identification of a dog based on its coat color is crucial, such as in dog shows, legal disputes, or for breed-specific registrations.
Overall, the discovery of the true color of dog skin has far-reaching implications for the world of dog breeding and selection. It not only allows breeders to explore new coat color possibilities but also aids in promoting the health and preservation of specific coat colors within breeds. This knowledge can contribute to advancements in the field of canine genetics and enhance our understanding of the intricate world of dog coat colors.
The true color of dog skin can vary depending on the breed and individual dog. It can range from pink to black, and may also have spots or patches of different colors.
Studying the color of dog skin is important for several reasons. It can help veterinarians detect certain health conditions, such as skin allergies or infections. It can also provide insights into the genetic makeup and ancestry of different dog breeds. Additionally, understanding the color of dog skin can help in the development of grooming and skincare products specifically designed for different types of dogs.
Yes, there can be specific patterns or markings on dog skin. Some dogs may have spots or patches of different colors on their skin. This can be especially common in breeds with a merle coat pattern, such as Australian Shepherds or Dalmatians. Other dogs may have pigmented areas or freckles on their skin.
Yes, the color of dog skin can change over time. In some cases, puppies may be born with lighter skin and as they grow, their skin may darken. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or with certain medical conditions, can also cause changes in the color of dog skin.
No, not all dogs have the same color of skin. The color of dog skin can vary greatly depending on the breed and individual dog. Some dogs may have pink skin, while others may have black or brown skin. There can also be variation in the color of the hair and the skin underneath.
The color of dog skin can affect their overall health in various ways. For example, dogs with lighter skin are more prone to sunburn and skin damage from UV rays. Dogs with darker skin have more protection against sunburn, but may be more prone to overheating in hot weather. The color of dog skin can also impact how easily skin issues, such as infections or allergies, are detected and treated.
Exo Dogs Introducing Exo Dogs: a groundbreaking innovation that merges the loyalty and intelligence of dogs with the cutting-edge technology of …
Read ArticleIs Hay Good For Dogs Dogs are known to have sensitive digestive systems, and it’s important for pet owners to provide them with a balanced and …
Read ArticleDo Dogs Drink More Water As They Get Older As dogs age, their bodies undergo several physiological changes. One of the most noticeable changes is …
Read ArticleWhat Foods Increase Red Blood Cells In Dogs Red blood cells play a crucial role in a dog’s overall health and well-being. These cells are responsible …
Read ArticleAre Blue Heelers Easy To Potty Train Potty training can be a challenging task for any dog owner, but it is particularly important for Australian …
Read ArticleHow To Make Dog Throw Up After Eating Chocolate Is your dog in danger after eating chocolate? Chocolate can be toxic to dogs and if your furry friend …
Read Article