Will a Male Dog Attack a Female Dog? Understanding Canine Aggression
Will A Male Dog Attack A Female Dog Dogs are generally social animals and can get along well with each other. However, canine aggression is not …
Read Article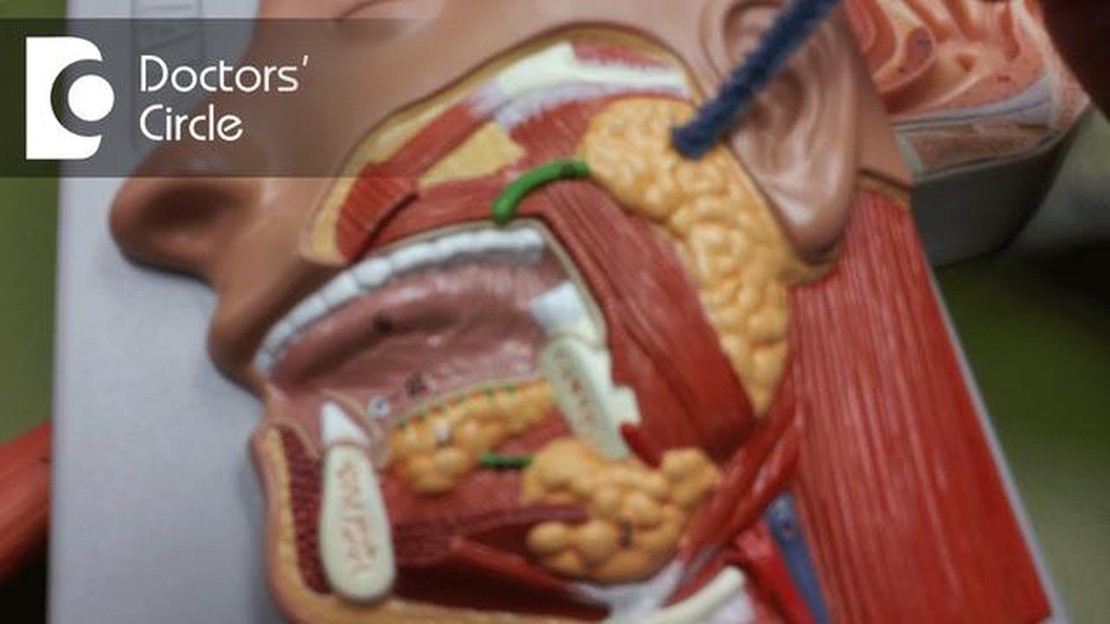
An obstructed salivary gland occurs when there is a blockage or obstruction in one of the salivary ducts, which prevents saliva from flowing freely. This condition can cause discomfort and pain, as well as other symptoms such as swelling and infection. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for an obstructed salivary gland is important for proper diagnosis and management of the condition.
There are several factors that can lead to the development of an obstructed salivary gland. One common cause is the formation of salivary stones, also known as sialoliths, which are hard deposits that can block the ducts. Other causes include infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, as well as certain medical conditions that affect the salivary glands, such as Sjögren’s syndrome or HIV/AIDS.
The symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include pain and swelling in the affected area, difficulty in swallowing or opening the mouth, and a dry mouth. In some cases, an infection may develop, leading to symptoms such as fever, redness, and pus draining from the gland.
Treatment options for an obstructed salivary gland depend on the cause and severity of the condition. In mild cases, simple home remedies such as warm compresses, drinking plenty of fluids, and sucking on sour candies or citrus fruits can help stimulate saliva production and alleviate symptoms. In more severe cases, medical intervention may be necessary, such as the use of antibiotics for bacterial infections, or surgical procedures to remove any blockages or stones.
In conclusion, an obstructed salivary gland can cause discomfort and pain, as well as other symptoms such as swelling and infection. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition in order to receive proper diagnosis and management. Home remedies can provide relief for mild cases, while more severe cases may require medical intervention. If you are experiencing symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
An obstructed salivary gland occurs when there is a blockage in the duct that carries the saliva from the gland to the mouth. This blockage can be caused by various factors, including:
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment if you suspect an obstructed salivary gland. The underlying cause of the obstruction will determine the best course of action to relieve symptoms and prevent further complications.
Saliva stones, also known as salivary stones or sialoliths, are calcified deposits that can form in the salivary glands. They are small, hard formations that can obstruct the flow of saliva, leading to blockages and various symptoms.
Saliva stones typically form in the ducts of the salivary glands, which are responsible for carrying saliva from the glands to the mouth. The exact cause of the formation of these stones is still unknown, but it is believed to be related to the buildup of minerals in the saliva or changes in the structure of the ducts.
When a saliva stone forms, it can block the flow of saliva, causing a range of symptoms. Some common symptoms include pain or swelling in the affected gland, difficulty or pain when opening the mouth or swallowing, dry mouth, foul taste or odor in the mouth, and infection in the gland.
The diagnosis of saliva stones is typically made through a physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound. Once diagnosed, treatment options can be discussed and recommended by a healthcare professional.
The treatment for saliva stones and blockages depends on the size and location of the stone. In some cases, smaller stones may pass on their own without intervention. However, larger stones or persistent blockages may require medical intervention.
One common treatment option is the manual removal of the stone through a procedure called sialolithotomy. This involves making a small incision in the affected duct and manually extracting the stone. Another option is the use of medications, such as antibiotics or steroids, to help reduce inflammation and promote the passage of the stone.
In some cases, if the blockage or stone is severe and causing recurrent symptoms, surgical removal of the affected gland may be necessary. This is typically a last resort option and is only considered when other treatments have failed or if there is a risk of complications.
To prevent the formation of saliva stones and blockages, maintaining good oral hygiene is important. This includes regular brushing and flossing, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol, which can contribute to dry mouth.
In conclusion, saliva stones and blockages can cause significant discomfort and symptoms. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or suspect a blockage. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options to alleviate the symptoms and prevent complications.
Infections and inflammation are common causes of obstruction in the salivary glands. When a salivary gland becomes infected or inflamed, it can lead to the blockage of saliva flow.
Infections: Salivary gland infections, also known as sialadenitis, occur when bacteria enter the gland and cause an infection. This can result in the gland becoming swollen and painful. The most common cause of salivary gland infections is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
Inflammation: Inflammation of the salivary glands, known as sialoadenitis, can occur due to various reasons, including viral infections, autoimmune conditions, or the presence of a salivary stone. The inflammation causes swelling and pain, leading to the obstruction of the gland.
In both cases, the obstruction of the salivary gland can cause symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing, pain or tenderness in the affected area, and swelling. The affected gland may also feel firm or hard to the touch.
Treatment: Infections and inflammation of the salivary glands are typically treated with antibiotics to eliminate the infection or reduce inflammation. Pain relievers may also be prescribed to alleviate the pain and discomfort. In some cases, warm compresses and massaging the affected gland can help to improve the flow of saliva and relieve the obstruction. Surgical intervention may be necessary in severe cases or when there is a presence of a salivary stone that cannot be removed non-invasively.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland, as prompt treatment can help to prevent complications and restore normal function to the gland.
Read Also: Why Do Dogs Walk Weird With Shoes: Understanding the Science Behind Canine Footwear
Tumors in the salivary glands can cause partial or complete obstruction of the saliva flow. There are different types of tumors that can develop in the salivary glands, including:
Common types of benign salivary gland tumors include pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin’s tumor, while malignant tumors include mucoepidermoid carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma.
When a tumor or growth develops in the salivary glands, it can cause various symptoms, such as:
If a tumor or growth is suspected, a healthcare professional may perform a physical examination, order imaging tests (such as CT or MRI scans), and recommend a biopsy to determine the nature of the tumor.
Common types of salivary gland tumors
| Type of Tumor | Description |
|---|---|
| Pleomorphic adenoma | The most common type of benign salivary gland tumor. It usually occurs in the parotid gland and can cause facial asymmetry. |
| Warthin’s tumor | A benign tumor that commonly affects the parotid gland. It is more common in males and is often associated with smoking. |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | A malignant tumor that can occur in any salivary gland. It is characterized by a mixture of mucous-producing and squamous cells. |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | A malignant tumor that often affects the submandibular or minor salivary glands. It is known for its slow growth rate and tendency to invade surrounding tissues. |
Read Also: Puppy Umbilical Cord Infection: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
The treatment of salivary gland tumors depends on various factors, including the type, location, and stage of the tumor. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Benign tumors are often treated with surgical removal, while malignant tumors may require a combination of treatments.
Regular check-ups and early detection are important for managing salivary gland tumors. If you notice any unusual symptoms or have concerns about your salivary glands, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
An obstructed salivary gland can cause a variety of symptoms. These symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage, as well as individual factors. Some common symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland include:
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, diagnose the cause of the obstruction, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Pain and swelling are common symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland. When a salivary gland becomes blocked, saliva cannot properly flow and can build up, causing pain and swelling in the affected area.
The pain associated with an obstructed salivary gland can range from mild discomfort to severe throbbing pain. It may be constant or come and go throughout the day. The pain is typically localized to the area near the affected gland, such as the cheek or jaw.
In addition to pain, swelling is another common symptom. The swollen area may feel tender to the touch and may appear red or inflamed. The swelling is usually localized to the specific gland that is blocked but can also affect surrounding tissues.
Other symptoms that may accompany pain and swelling include:
If the obstructed salivary gland becomes infected, symptoms may worsen and include fever, chills, and an abscess or pus-filled swelling.
If you are experiencing pain and swelling in the area of a salivary gland, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can examine the area and determine the underlying cause of the obstruction. Treatment options may include home remedies, such as warm compresses and increased fluid intake, or more advanced interventions, such as medication or surgery.
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a condition that occurs when the salivary glands do not produce enough saliva. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by lubricating the mouth and aiding in the process of swallowing. When there is a lack of saliva, it can lead to difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia.
There are several causes of dry mouth and difficulty swallowing. One common cause is medication side effects. Certain medications, such as antihistamines, antidepressants, and decongestants, can cause a decrease in saliva production. Additionally, medical conditions such as Sjogren’s syndrome, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS can also contribute to dry mouth.
The symptoms of dry mouth and difficulty swallowing can include:
Treatment for dry mouth and difficulty swallowing primarily focuses on addressing the underlying cause. This may involve adjusting medication dosages or switching to different medications. Drinking plenty of water and staying hydrated can also help alleviate dry mouth symptoms. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candies can stimulate saliva production. In some cases, saliva substitutes may be prescribed to help keep the mouth moisturized.
If left untreated, dry mouth and difficulty swallowing can lead to further complications, such as tooth decay, oral infections, and difficulty maintaining a healthy diet. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if experiencing persistent dry mouth or difficulty swallowing.
An obstructed salivary gland can be caused by a variety of factors, including the formation of a stone or blockage in the ducts that carry saliva. Other possible causes include infections, tumors, and certain medical conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome.
The symptoms of an obstructed salivary gland may include swelling and pain in the area of the affected gland, difficulty or pain while eating or swallowing, dry mouth, and a foul taste in the mouth. In some cases, a visible lump or mass may be present.
To diagnose an obstructed salivary gland, a healthcare professional may perform a physical examination of the affected area and ask about the symptoms. They may also order imaging tests such as a CT scan or ultrasound to determine the location and cause of the blockage.
The treatment for an obstructed salivary gland depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, conservative measures such as warm compresses, massage, and increased fluid intake may be recommended to help alleviate the blockage. Other treatment options may include medication to reduce inflammation or surgery to remove the blockage or affected gland.
Yes, in some cases, an obstructed salivary gland can lead to complications such as the development of an infection or abscess, which may require further treatment with antibiotics or drainage. If left untreated, the blockage may also cause long-term damage to the gland, which can affect saliva production.
Will A Male Dog Attack A Female Dog Dogs are generally social animals and can get along well with each other. However, canine aggression is not …
Read ArticleWhat Material Can Dogs Not Smell Through When it comes to the sense of smell, dogs are truly remarkable creatures. Their olfactory receptors are …
Read ArticleWhy Are Small Dogs So Annoying Small dogs can be a handful. They bark incessantly, jump on furniture, and seem to have boundless energy. Some people …
Read ArticleDulcolax For Dogs Introducing Dulcolax for Dogs - the trusted solution for your furry friend’s digestive health. Whether your dog is experiencing …
Read ArticleIs Iams Wsava Approved Are you looking for a pet food brand that prioritizes your pet’s health and well-being? Look no further than Iams! With their …
Read ArticleWhy Does My Dog Snap At My Face Having a dog that snaps at your face can be a terrifying experience for both you and your furry friend. It’s important …
Read Article