Dog Safe Paint For Paws: How to Keep Your Pet's Paws Colorful and Safe
Dog Safe Paint For Paws Are you tired of your furry friend’s paws always looking plain and boring? Do you want to add a splash of color to their …
Read Article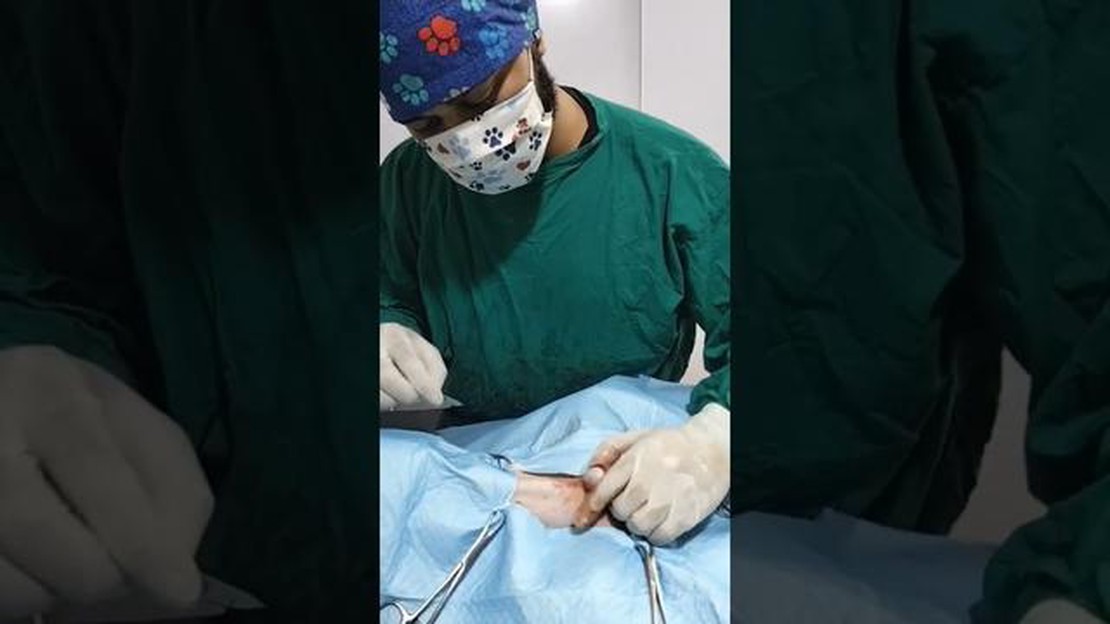
If you are a dog owner considering neutering your pet, you may be curious about whether or not a neutered dog can still produce sperm. While neutering is a common procedure that is performed to prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduce certain behavioral issues, it does have an impact on a dog’s reproductive capabilities.
Neutering, also known as castration, involves the surgical removal of a male dog’s testicles. This procedure is typically done to eliminate the production of testosterone, which is responsible for driving many male reproductive behaviors. Without testicles, a neutered dog no longer has the ability to produce sperm.
However, it is important to note that the effects of neutering can vary depending on the age at which the procedure is performed. Dogs that are neutered before reaching sexual maturity may not have fully developed reproductive organs, and as a result, they may not produce sperm even before being neutered. On the other hand, dogs that are neutered after reaching sexual maturity may have already developed the ability to produce sperm, and therefore, may continue to do so for some time after being neutered.
It is also worth noting that in rare cases, a neutered dog may still be able to produce a small amount of sperm due to incomplete removal of the testicles during the neutering procedure. This is why it is important to choose a reputable veterinarian who has experience performing neutering surgeries.
In conclusion, while the primary purpose of neutering is to eliminate a dog’s ability to reproduce, it is possible for a neutered dog to still produce sperm in certain circumstances. If you have any concerns about your dog’s reproductive capabilities after neutering, it is best to consult with a veterinarian.
Neutering is a common surgical procedure that removes the reproductive organs of male dogs. It is also known as castration or gonadectomy. Here is an overview of the process:
Note: The process of neutering may vary depending on the veterinarian’s technique and the dog’s specific needs. It is always best to follow your veterinarian’s instructions and ask any questions you may have.
Neutering, also known as castration, is a common surgical procedure that involves the removal of a male dog’s testicles. This procedure is performed by a veterinarian and is typically done to prevent reproduction or to treat certain medical conditions.
One of the primary effects of neutering is the cessation of sperm production. Since the testicles are removed, the dog will no longer be able to produce sperm. This means that neutered dogs cannot impregnate females.
When a dog is neutered, the testicles are removed, which affects the hormone production in the body. Testosterone, the hormone responsible for sperm production, is significantly reduced. As a result, the dog’s body no longer produces sperm.
It is important to note that although neutering eliminates sperm production, it does not immediately eliminate existing sperm in the reproductive system. Sperm can live in the reproductive tract for a certain period of time, so there is still a small chance of fertilizing a female if the dog has recently been neutered.
Neutering also has other effects on a dog’s behavior and health. It can help reduce aggression, roaming, and marking behaviors. Additionally, neutering can lower the risk of certain diseases, such as testicular cancer and prostate problems.
Neutering has several benefits for both dogs and their owners. Some of these benefits include:
If you are considering neutering your dog, it is important to consult with a veterinarian. They can provide you with more information about the procedure, as well as discuss any potential risks or concerns specific to your dog’s breed or age.
Neutering is generally considered safe and beneficial for most dogs, but it is always best to consult with a professional to ensure the health and well-being of your pet.
There are several common misconceptions surrounding the topic of neutered dogs and sperm production. Let’s take a closer look at these misconceptions and debunk them:
This is not entirely true. While neutering involves removing the testicles, which are responsible for producing sperm, some dogs may still have residual sperm in their reproductive tract for a short period of time after the procedure. However, over time, the production of new sperm ceases completely, and the remaining sperm will eventually be reabsorbed by the dog’s body. 2. Neutered dogs can impregnate female dogs.
This is a misconception. Once a dog is neutered, it becomes sterile and cannot impregnate a female dog. The removal of the testicles eliminates the source of sperm, making it impossible for a neutered dog to fertilize eggs and reproduce. 3. Neutered dogs still experience sexual arousal.
While neutering reduces the sex drive in dogs, it does not eliminate sexual arousal completely. Neutered dogs may still show signs of sexual interest, such as mounting or humping behavior, but without the ability to reproduce. This behavior is typically driven by other factors, such as dominance or playfulness, rather than the desire to mate. 4. Neutering affects a dog’s overall health negatively.
This is a common misconception. Neutering has several health benefits for dogs, including the prevention of certain diseases, such as testicular cancer and uterine infections. It can also reduce the risk of behavioral issues, such as aggression and roaming. However, it is important to consult with a veterinarian to weigh the potential risks and benefits of neutering for each individual dog.
Summary of Common Misconceptions
Read Also: When Can I Bathe My Dog After Surgery? - Everything You Need to Know
| Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| Neutered dogs cannot produce any sperm. | Neutering eliminates the production of new sperm, but residual sperm may be present for a short period of time. |
| Neutered dogs can impregnate female dogs. | Neutered dogs are sterile and cannot impregnate female dogs. |
| Neutered dogs still experience sexual arousal. | Neutered dogs may show signs of sexual arousal, but they are unable to reproduce. |
| Neutering affects a dog’s overall health negatively. | Neutering has several health benefits and can prevent certain diseases and behavioral issues. |
It is important to have accurate information about neutering and sperm production in dogs to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Neutering, also known as spaying (for females) or castrating (for males), is a common surgical procedure in which a dog’s reproductive organs are removed. This procedure is often done to help control overpopulation and unwanted breeding. Neutering has several effects on a dog’s fertility and reproductive health.
Effect on Sperm Production:
Read Also: Bernese Mountain Dog Not Eating: Causes, Tips, and Solution
Neutering a male dog involves removing the testicles, which are responsible for producing sperm. As a result, neutered dogs are unable to produce sperm and are considered sterile. However, it’s important to note that some dogs may still have residual sperm in their reproductive system immediately after the procedure. Therefore, it’s recommended to keep a neutered dog separate from intact females for a period of time to avoid any accidental breeding.
Effect on Hormonal Changes:
Neutering also affects a dog’s hormonal balance. Testosterone, the male hormone responsible for behaviors like marking, roaming, and aggression, is significantly reduced after neutering. This can lead to a decrease in these behaviors and can make a neutered male dog more calm and manageable. However, it’s important to note that neutering does not always completely eliminate these behaviors, as individual dogs may still exhibit them to some degree.
Health Benefits of Neutering:
Neutering can have several health benefits for dogs. It helps prevent certain reproductive diseases, like testicular cancer in males and pyometra (a life-threatening infection of the uterus) in females. Neutered dogs also have a reduced risk of developing prostate problems and certain types of tumors. Additionally, neutering can help prevent behavioral issues related to mating instincts, such as aggression, roaming, and excessive mounting.
Recovery and Aftercare:
After the neutering procedure, dogs may experience some pain and discomfort. It’s important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions for pain management and provide a safe and quiet space for the dog to rest and recover. It’s also important to prevent the dog from licking or biting at the incision site, as this can lead to infection. Regular post-operative check-ups are usually recommended to monitor the dog’s healing process.
Conclusion:
Neutering a dog has significant effects on their fertility and reproductive health. Neutered dogs are unable to produce sperm and are considered sterile. Additionally, neutering can provide numerous health benefits and help prevent certain diseases. It’s important to consult with a veterinarian to determine the best time to neuter a dog and to ensure a smooth recovery process.
If you have any concerns or questions about your neutered dog’s reproductive capabilities, it is always best to consult with a veterinarian. They are the experts in animal health and will be able to provide you with accurate information and advice based on your specific dog’s circumstances.
A veterinarian will be able to explain the neutering procedure in detail and how it affects a dog’s reproductive system. They can also provide information on any potential risks or complications that may arise after the procedure.
If you are still unsure about whether a neutered dog can produce sperm, a veterinarian can perform a thorough examination and diagnostic tests to determine the status of your dog’s reproductive organs.
Additionally, a veterinarian can provide guidance on post-neutering care and any necessary lifestyle adjustments to ensure your dog’s overall health and well-being. They can answer any questions you may have regarding behavior, hormonal changes, or any other concerns related to your neutered dog.
Remember that every dog is unique, and the effects of neutering can vary from one individual to another. By consulting a veterinarian, you will receive the most accurate and tailored information for your dog’s specific situation.
No, neutered dogs cannot produce sperm. Neutering involves removing the testicles, which are responsible for producing sperm.
No, it is not possible for a neutered dog to impregnate a female dog. Neutered dogs do not have the ability to produce sperm, which is necessary for reproduction.
Some people may believe that neutered dogs can still produce sperm because they may observe certain behaviors, such as mounting or humping, which are associated with sexual behavior. However, these behaviors are not necessarily indicative of sperm production.
Neutering a dog has several benefits, including preventing unwanted litters, reducing the risk of certain cancers and diseases, and improving behavior, such as reducing aggression and roaming tendencies.
A dog can usually be neutered between the ages of 6 to 9 months. However, the exact age varies depending on the breed and individual dog. It is best to consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate age for neutering.
Dog Safe Paint For Paws Are you tired of your furry friend’s paws always looking plain and boring? Do you want to add a splash of color to their …
Read ArticleIs Human Saline Solution Safe For Dogs Eyes As dog owners, we want to provide the best care for our furry friends, including their eye health. It’s …
Read ArticleAre Huskies Good Farm Dogs When it comes to choosing a farm dog, there are many factors to consider. One breed that often comes up in the discussion …
Read ArticleAre Dog Teeth Stronger Than Human When it comes to the strength of teeth, many people wonder if dog teeth are stronger than human teeth. After all, …
Read ArticleOld Dog Losing Weight Drinking Lots Water An old dog losing weight and drinking excessive amounts of water can be a cause for concern for pet owners. …
Read ArticleIs Highlighter Toxic Highlighters are a common tool used to emphasize important information in textbooks, notes, and documents. However, there have …
Read Article