Does Greyhound Have Bathrooms: A Comprehensive Guide
Does Greyhound Have Bathrooms Greyhound is one of the most popular bus transportation companies in the United States. Many travelers choose Greyhound …
Read Article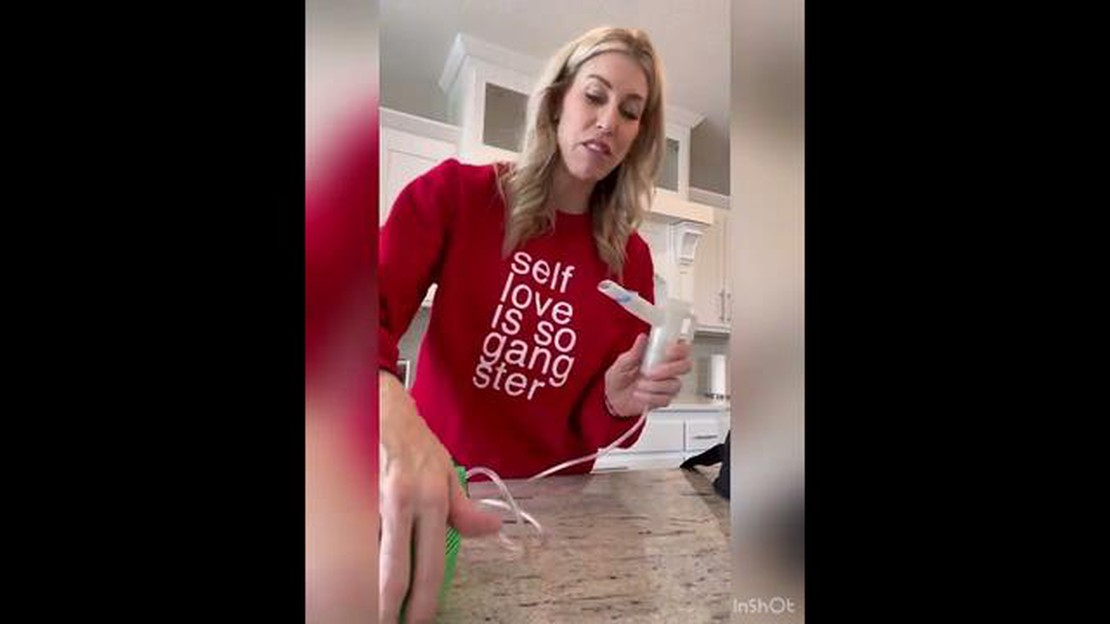
Breathing issues can be a cause for concern for any pet owner, and it’s only natural to want to provide relief for your furry friend. One question that often arises is whether or not it’s safe to give your dog a breathing treatment.
To answer this question, it’s important to understand what a breathing treatment entails. Breathing treatments, also known as nebulization, involve the inhalation of medicated mist through a mask or tube. They are commonly used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and allergies in humans.
While humans can benefit from breathing treatments, the same cannot always be said for our canine companions. Dogs have different respiratory systems and can react differently to medications than humans. It’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian before attempting to administer a breathing treatment to your dog.
The veterinarian will provide expert advice and guidelines specific to your dog’s health condition. They will determine whether or not a breathing treatment is appropriate and which medications, if any, should be used. It’s important to follow their instructions carefully to ensure the safety and well-being of your beloved pet.
If your dog is having difficulty breathing, it can be a worrying and distressing situation. Breathing problems can be caused by various factors, including respiratory infections, allergic reactions, or underlying health conditions. In some cases, your veterinarian may recommend a breathing treatment as a part of the treatment plan for your dog.
A breathing treatment, also known as nebulization or aerosol therapy, involves using a device called a nebulizer to deliver medication directly into your dog’s airways. The medication is typically diluted with saline solution and converted into a fine mist that your dog can inhale. This method can be especially effective for treating respiratory issues such as bronchitis, pneumonia, or asthma.
It is important to note that you should never attempt to give your dog a breathing treatment without consulting your veterinarian. Your vet will assess your dog’s condition and prescribe the appropriate medication and dosage. Giving the wrong medication or incorrect dosage can be harmful to your dog and may worsen their condition. Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions and ask for clarification if you have any doubts.
When administering a breathing treatment to your dog, it is essential to create a calm and quiet environment to minimize stress. Place the nebulizer near your dog’s nose or use a mask specifically designed for animals. Allow your dog to inhale the mist for the recommended duration, which is typically a few minutes. It may be helpful to distract your dog with treats or toys during the treatment to keep them calm and cooperative.
After the breathing treatment, monitor your dog for any adverse reactions or changes in breathing. If you notice any concerning symptoms or if your dog’s condition does not improve, contact your veterinarian for further guidance.
Key Points to Remember:
Remember, it is always best to seek professional veterinary advice for your dog’s health concerns. Your veterinarian is the most qualified person to diagnose and treat your dog’s breathing problems, and they can provide you with appropriate guidance and treatment options.
When it comes to giving your dog a breathing treatment, it is always best to seek advice from a veterinarian. They will be able to provide you with expert guidance on how to administer the treatment and what medications or therapies may be necessary.
Here are some general guidelines to keep in mind:
Remember, every dog is unique, and their respiratory needs may vary. It is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to ensure your dog receives the best possible care and treatment for their specific condition.
Just like humans, dogs can experience various breathing problems that may range from mild to severe. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these issues and understand the possible causes and treatments.
1. Nasal congestion: Dogs may experience nasal congestion due to allergies, respiratory infections, foreign objects stuck in the nose, or anatomical abnormalities. Signs of nasal congestion include snoring, snorting, difficulty breathing through the nose, and discharge from the nose.
2. Asthma: Some dogs can develop asthma, which is a chronic inflammation of the airways. Asthma attacks can be triggered by allergens, pollutants, or exercise. Dogs with asthma may show symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, rapid breathing, and difficulty catching their breath.
3. Kennel cough: Kennel cough, also known as infectious tracheobronchitis, is a highly contagious respiratory infection that can cause coughing, gagging, and difficulty breathing. It is commonly spread in places where dogs are in close proximity, such as boarding kennels or dog parks.
4. Collapsed trachea: Small dog breeds, such as Chihuahuas and Yorkshire Terriers, are prone to a condition called collapsed trachea. In this condition, the cartilage rings that support the trachea become weak, leading to coughing, wheezing, and respiratory distress.
5. Pneumonia: Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs that can cause breathing difficulties in dogs. It is often caused by bacteria, viruses, or aspiration of foreign objects. Symptoms may include coughing, rapid breathing, lethargy, loss of appetite, and fever.
To properly diagnose and treat dog breathing problems, it is essential to consult with a veterinarian. They can perform a thorough examination, order diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include medications, breathing treatments, or surgery in severe cases.
Preventing Dog Breathing Problems:
- Keep your dog’s environment clean and free from respiratory irritants.
Read Also: Can Dogs Eat Cooked Chicken? A Guide to Feeding Your Canine Friend
By understanding the common breathing problems that dogs can experience and taking preventive measures, you can help ensure your furry friend enjoys optimal respiratory health.
Read Also: Are Crayons Toxic To Dogs? Exploring the Potential Hazards for Your Furry Friend
If you notice that your dog is experiencing difficulty breathing, it’s important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. While a breathing treatment may not always be necessary, it can be a helpful tool in managing respiratory issues in dogs. There are several circumstances in which your dog may require a breathing treatment:
It’s important to remember that a breathing treatment is not a cure for underlying respiratory issues in dogs. It is a management tool that can provide temporary relief and improve symptoms. Always consult with your veterinarian before administering any breathing treatments to ensure it is appropriate for your dog’s specific condition. They can provide guidance on the best course of action and demonstrate proper technique for administering the treatment.
When a dog is experiencing respiratory difficulties or is diagnosed with a respiratory condition, breathing treatments can be recommended by a veterinarian. These treatments can help alleviate symptoms and improve the dog’s overall breathing function. There are several types of breathing treatments available for dogs, each serving a different purpose.
1. Nebulization: Nebulization is a common breathing treatment for dogs that involves administering medication in the form of a mist. This mist is created by a nebulizer, a device that converts liquid medication into a fine mist that the dog can inhale. Nebulization is often used to deliver bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antibiotics directly to the lungs.
2. Inhalers: Inhalers are another type of breathing treatment that can be used for dogs with respiratory conditions. These devices deliver medication in the form of a spray or powder that the dog can inhale. Inhalers are often used to administer bronchodilators or corticosteroids to manage asthma or other respiratory diseases.
3. Oxygen Therapy: Oxygen therapy is a breathing treatment that involves providing the dog with supplemental oxygen. This can be done through a mask or nasal cannula placed over the dog’s nose and mouth. Oxygen therapy is commonly used in cases of respiratory distress or when a dog is having difficulty breathing due to conditions such as pneumonia or heart failure.
4. Positive Pressure Ventilation: Positive pressure ventilation is a breathing treatment that uses a mechanical ventilator to assist the dog’s breathing. This treatment is typically used in cases of severe respiratory distress, such as during a surgical procedure or in the intensive care unit. The ventilator delivers pressurized air into the lungs, helping to expand them and improve oxygenation.
5. Chest Physiotherapy: Chest physiotherapy is a non-invasive breathing treatment that involves manual techniques to help clear mucus and secretions from the dog’s lungs. This can include techniques such as percussion, vibration, and postural drainage. Chest physiotherapy can be helpful for dogs with conditions such as pneumonia or chronic bronchitis.
6. Medication Administration: In addition to specific breathing treatments, dogs with respiratory conditions may also require medication administration. This can include oral medications, injections, or topical treatments to help manage underlying conditions or symptoms.
It is important to note that breathing treatments for dogs should always be prescribed and supervised by a veterinarian. They will determine the appropriate treatment based on the dog’s specific condition and needs. Following the veterinarian’s guidelines and recommendations is essential for the dog’s health and well-being.
If your dog has a respiratory condition that requires a breathing treatment, it’s important to know how to administer it properly. Here are some guidelines to help you:
Remember to consult with your veterinarian for specific instructions and guidance on how to administer a breathing treatment to your dog. They will be able to provide you with personalized advice based on your dog’s condition and medical history.
Yes, it can be safe to give your dog a breathing treatment, but it should only be done under the guidance of a veterinarian. They will be able to determine the underlying cause of your dog’s breathing difficulties and recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
There are several types of breathing treatments that can be given to dogs, including inhalers, nebulizers, and steam therapy. The specific treatment recommended for your dog will depend on their individual needs and the underlying cause of their breathing difficulties.
You should consider giving your dog a breathing treatment if they are experiencing difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, or any other respiratory symptoms. However, it is important to consult with a veterinarian before starting any treatment to ensure that it is appropriate for your dog’s specific condition.
In some cases, you may be able to give your dog a breathing treatment at home under the guidance of a veterinarian. They will be able to show you how to properly administer the treatment and monitor your dog’s progress. However, it is important to follow their instructions closely and seek immediate veterinary care if your dog’s condition worsens.
Potential side effects of breathing treatments for dogs can include increased heart rate, restlessness, coughing, or difficulty breathing. It is important to closely monitor your dog during and after the treatment and contact your veterinarian if these side effects occur or worsen.
While some respiratory conditions in dogs are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk. This includes keeping your dog’s environment clean and free of irritants, avoiding exposure to smoke or other pollutants, and ensuring they receive regular veterinary check-ups to catch any potential issues early.
Does Greyhound Have Bathrooms Greyhound is one of the most popular bus transportation companies in the United States. Many travelers choose Greyhound …
Read ArticleWhat Does Dog Sperm Look Like When it comes to understanding the reproductive system of dogs, there is a lot of misinformation and confusion. One …
Read ArticleHigh Strung Dog Breeds Do you have a high-energy dog? Are you struggling to keep up with their endless enthusiasm? Look no further! Our team at …
Read ArticleIs Dog Chow Good For Dogs When it comes to feeding our furry friends, it’s important to make sure we are providing them with the best nutrition …
Read ArticleDoes Wetting A Dog Cool It Down Dogs, just like humans, can become overheated in hot weather, and it is important for pet owners to understand how to …
Read ArticleIs Purina Moist And Meaty Bad For Dogs Many dog owners wonder whether the popular dog food brand, Purina Moist and Meaty, is bad for their furry …
Read Article