Understanding the Consequences of Separating a Puppy from Its Mother Too Early
What Happens If You Take A Puppy Away From Its Mother Too Early Introduction: Table Of Contents Why Separating a Puppy Early Can Have Serious …
Read Article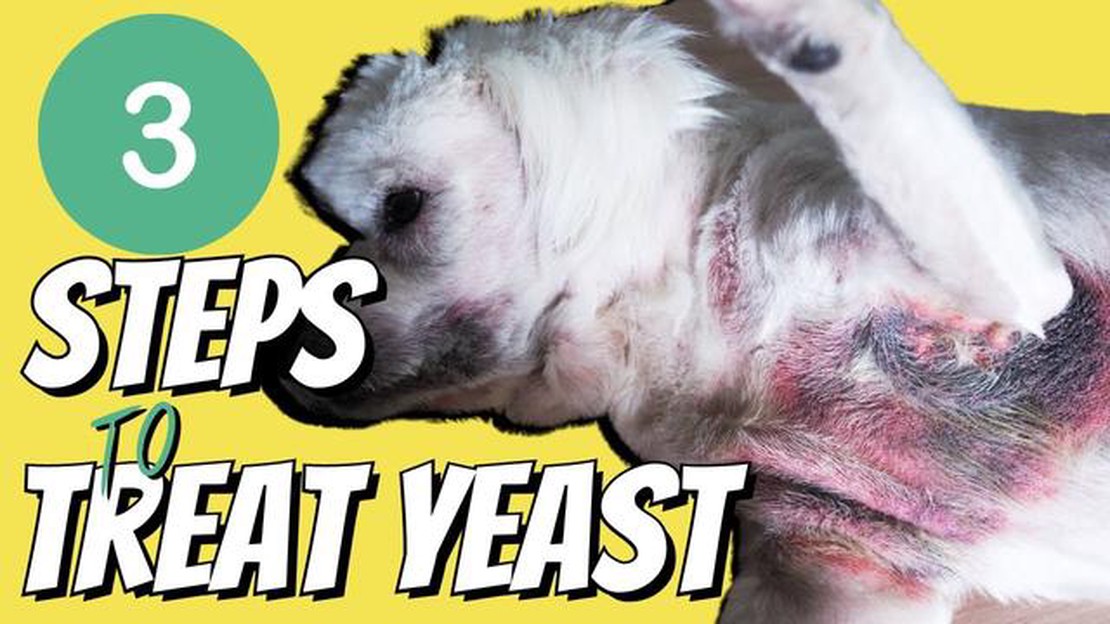
Yeast infections can be quite common in dogs, especially in their ears, paws, and skin folds. While these infections are not typically life-threatening, they can cause discomfort and irritation for your furry friend. But can humans also contract yeast infections from dogs?
The good news is that it is highly unlikely for humans to get yeast infections from dogs. Yeast infections are caused by a specific type of fungus called Candida, which is commonly found in the environment. While dogs can carry this fungus on their skin and in their ears, it is rare for it to be transmitted to humans.
However, it is important to note that there have been a few isolated cases where humans have developed yeast infections after close contact with dogs. This usually occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplant recipients. In these cases, it is crucial to seek medical attention and follow proper hygiene practices to prevent the spread of infection.
To protect both yourself and your furry companion, it is best to practice good hygiene and regularly clean your dog’s ears, paws, and skin folds. If you notice any signs of a yeast infection in your dog, such as itching, redness, or a foul odor, consult your veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Yeast infection, also known as Candidiasis, is a common fungal infection that can affect dogs. It is caused by the overgrowth of yeast organisms, particularly the fungus Candida Albicans, on the skin or mucous membranes of the dog.
Dogs naturally have yeast organisms on their skin and in their bodies, but under certain conditions, such as a weakened immune system or imbalanced gut flora, the yeast can multiply rapidly and cause an infection. Yeast infections can occur in various parts of a dog’s body, including the ears, paws, genital area, and folds of the skin.
Some of the common symptoms of yeast infection in dogs include:
Factors that can contribute to the development of yeast infection in dogs include:
It is important to consult a veterinarian if you suspect that your dog has a yeast infection. The veterinarian can perform a physical examination, collect samples for laboratory testing, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Treatment for yeast infection in dogs may involve topical antifungal medications, oral medications, special shampoos or ear cleaners, and dietary changes.
Preventing yeast infections in dogs involves maintaining good hygiene, keeping the dog’s skin clean and dry, providing a nutritious diet, and addressing any underlying health conditions. Regular grooming, including cleaning the ears and paws, can help prevent the overgrowth of yeast organisms.
In summary, yeast infection is a common fungal infection that can affect dogs. It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek veterinary care for proper diagnosis and treatment. By taking preventive measures and maintaining good hygiene, you can help keep your dog healthy and free from yeast infections.
Yeast infection in dogs, also known as canine candidiasis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast called Malassezia. This yeast is naturally found in small amounts on your dog’s skin, ears, and digestive tract.
However, certain factors can disrupt the natural balance of yeast in your dog’s body, leading to an overgrowth and the development of a yeast infection. Some common causes of yeast infection in dogs include:
If your dog is experiencing symptoms of a yeast infection, such as itching, redness, odor, or discharge, it’s important to consult with your veterinarian. They can diagnose the infection and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include topical or oral antifungal medications, dietary changes, and addressing any underlying issues that may be contributing to the infection.
Preventing yeast infections in dogs involves maintaining a healthy diet, keeping your dog’s skin clean and dry, regularly grooming your dog, and addressing any underlying health conditions or allergies. Ensuring your dog’s immune system is strong can also help prevent yeast overgrowth.
Yeast infection in dogs can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on the affected area of the body. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Prompt treatment can help alleviate discomfort and prevent the infection from worsening.
Read Also: Understanding Geico Homeowners Insurance Dog Breed Restrictions: What You Need to Know
Yeast infections are a common problem among dogs, and many pet owners worry about whether or not they can contract the infection from their furry friends. The good news is that while it is possible for humans to develop a yeast infection, it is highly unlikely to occur as a result of contact with an infected dog.
Yeast infections in dogs are typically caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which is naturally present in a dog’s body. Factors such as a weakened immune system, allergies, and the use of certain medications can contribute to the development of a yeast infection in dogs. Common symptoms include itching, redness, and a foul odor coming from the affected area.
However, the fungal strains that cause yeast infections in dogs are typically different from those that affect humans. While it is possible for a person to develop a yeast infection from contact with an infected dog, it is rare and usually only occurs in individuals with compromised immune systems.
If you are concerned about the possibility of contracting a yeast infection from your dog, there are several steps you can take to minimize the risk:
If you notice signs of a yeast infection in your dog, such as excessive itching or redness, it is important to consult with your veterinarian. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options. Remember, while it is possible for humans to develop a yeast infection, the chances of contracting one from your dog are minimal.
A yeast infection in dogs, also known as yeast dermatitis or Malassezia dermatitis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the dog’s skin. While yeast infections are common in dogs, many pet owners are concerned about whether these infections can be transmitted to humans.
Read Also: Are Labs Medium Or Large Dogs - Size Guide and Comparison
The good news is that yeast infections in dogs are generally not contagious to humans. The specific type of yeast that affects dogs, Malassezia, is not known to be zoonotic, which means it cannot be transmitted between animals and humans. Therefore, you do not have to worry about catching a yeast infection from your dog.
However, it is important to note that while the yeast itself may not be contagious, the underlying conditions that contribute to yeast overgrowth in dogs can sometimes be shared between pets and their owners. For example, both dogs and humans can develop yeast infections as a result of an underlying immune system disorder or an imbalance in the body’s natural flora.
If you suspect that your dog has a yeast infection, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Your vet can recommend the appropriate treatment plan, which may include medicated shampoos, topical creams, or oral medications to help clear up the infection.
To prevent yeast infections in dogs, it is important to keep your pet’s skin clean and dry, and to avoid over-bathing, as excessive moisture can create an environment for yeast to thrive. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and providing regular grooming can help support your dog’s overall skin health.
In conclusion, yeast infections in dogs are generally not contagious to humans. While it is possible for both dogs and humans to develop yeast infections, the specific types of yeast that affect each species are typically different. However, if you have concerns about your dog’s health or suspect they may have a yeast infection, it is always best to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Yeast infections can be uncomfortable and painful for dogs, and it’s important for pet owners to take steps to prevent them. Here are some tips to help prevent yeast infections in dogs:
By following these preventive measures, you can help keep your dog healthy and free from yeast infections. However, if your dog does develop a yeast infection, it is important to seek veterinary care for proper diagnosis and treatment.
If you suspect that you or your dog may have a yeast infection, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are a few signs that indicate it is time to visit a healthcare professional:
A healthcare professional can properly diagnose a yeast infection and recommend the appropriate treatment options for both you and your dog. They may also be able to provide guidance on preventive measures and lifestyle changes to help reduce the likelihood of future infections.
Yes, humans can get yeast infections from dogs. The most common way is through direct contact with an infected dog or by coming into contact with their contaminated environment.
The symptoms of yeast infection in humans can vary depending on the affected area, but common symptoms include itching, redness, swelling, and a white, cottage cheese-like discharge. Other symptoms may include a burning sensation, pain during intercourse, and a rash.
To prevent getting yeast infections from dogs, it is important to practice good hygiene. This includes washing your hands after handling dogs, especially if they have a known yeast infection, and avoiding direct contact with their contaminated areas. It is also recommended to keep your dog’s environment clean and dry to prevent the spread of yeast.
Yes, a yeast infection from a dog can be treated. The treatment will depend on the severity and location of the infection. In most cases, antifungal medications, such as creams or oral medications, are used to treat the infection. It is important to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Yes, a yeast infection in dogs can be contagious to humans. Humans can get infected through direct contact with an infected dog, such as touching their contaminated skin or fur. It is important to take precautions to prevent the spread of infection, especially if you have a weakened immune system.
No, dogs cannot transmit yeast infections sexually to humans. Yeast infections are caused by specific strains of yeast that are typically found in the environment or on human and animal bodies. Sexual transmission of yeast infections is not possible between different species.
If you suspect you have a yeast infection from your dog, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. They may recommend antifungal medications or other treatments to help clear the infection. It is also important to address any underlying factors that may be contributing to the infection, such as keeping your dog’s environment clean and addressing any underlying health issues in your dog.
What Happens If You Take A Puppy Away From Its Mother Too Early Introduction: Table Of Contents Why Separating a Puppy Early Can Have Serious …
Read ArticleCan Dogs Eat Beef Feet Are you wondering if it’s safe to feed your dog beef feet? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide, we’ll answer all your …
Read ArticleWhat Is A Blue Dog Worth Are you curious about the value of Blue Dog artworks? Look no further! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating …
Read ArticleCan Guanfacine Kill A Dog Guanfacine is a medication that is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat a variety of conditions in dogs, including …
Read ArticleCan You Put Lotion On Dogs As pet owners, we always want to ensure the well-being and comfort of our beloved furry friends. One question that often …
Read ArticleHow Soon After Death Can A Cadaver Dog Detect When a person dies, their body goes through a series of stages of decomposition. During this process, …
Read Article