Can Dogs Smell Through Vacuum Sealed Bags? The Surprising Truth Revealed
Can Dogs Smell Through Vacuum Sealed Bags Have you ever wondered if your furry friend can detect the scent of something sealed in a vacuum sealed bag? …
Read Article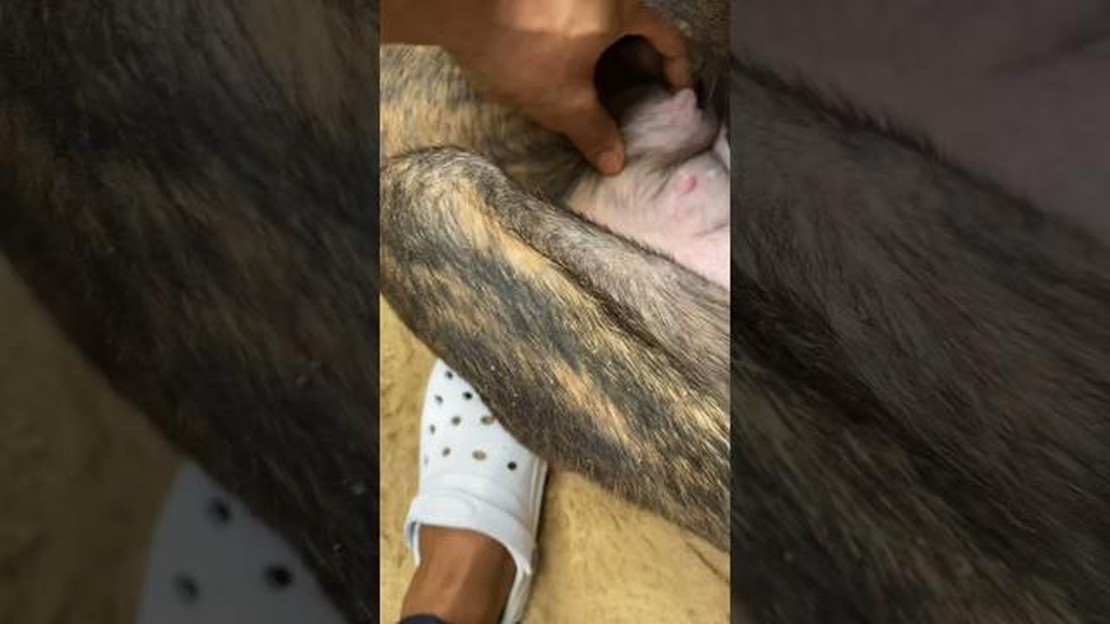
One of the most common questions that dog owners have is whether their female dogs can produce milk without being pregnant. This is a natural and understandable concern, as it can be alarming to see your dog producing milk when you know she hasn’t been bred.
The answer to this question is yes, dogs can indeed produce milk even if they are not pregnant. This phenomenon is known as false pregnancy or pseudopregnancy, and it is more common in certain breeds, such as Labradors, Beagles, and Dachshunds.
During false pregnancy, a dog’s body undergoes hormonal changes that mimic those of a real pregnancy. These hormonal fluctuations can cause the mammary glands to produce milk. This can be confusing for both the dog and the owner, as the dog may exhibit signs of maternal behavior, such as nesting, nursing stuffed animals, and even producing milk. However, there is no pregnancy and no puppies involved.
It is important to note that false pregnancy is a natural occurrence and not a health concern in most cases. The milk produced during this time is safe for the dog to consume, although it is not necessary for her to do so. However, if you notice any signs of discomfort or distress in your dog during a false pregnancy, it is always best to consult with your veterinarian for further guidance.
While it is commonly known that female dogs produce milk to nurse their puppies, it is also possible for dogs to produce milk without being pregnant. This phenomenon, known as false pregnancy or pseudopregnancy, occurs when a dog’s body goes through hormonal changes that mimic the symptoms of pregnancy.
During a false pregnancy, a female dog may experience enlargement of the mammary glands, nipple discharge, and even produce milk. This phenomenon typically occurs around 6 to 12 weeks after the dog’s last heat cycle and can last for several weeks.
The exact cause of false pregnancy in dogs is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal imbalances. The hormone prolactin, which is responsible for stimulating milk production in pregnant females, is also present during false pregnancy. Additionally, increased levels of progesterone, a hormone associated with pregnancy, can also contribute to the production of milk.
It is important for dog owners to be aware of the signs of false pregnancy as it can sometimes be mistaken for a real pregnancy. The dog may exhibit nesting behavior, display maternal instinct towards toys or objects, and even show signs of mild lactation. However, it is crucial to note that false pregnancy is a natural phenomenon and does not pose any health risks to the dog.
If a dog is experiencing false pregnancy and producing milk, it is not necessary to intervene or provide any special care. The milk produced during false pregnancy is usually not sufficient in quantity or nutritional value to sustain a litter of puppies. However, some dogs may experience discomfort or inflammation in the mammary glands. In such cases, consulting a veterinarian is recommended to provide appropriate treatment and relief for the dog.
In conclusion, while it may seem unusual for dogs to produce milk without being pregnant, it is a natural and relatively common phenomenon known as false pregnancy. Understanding this phenomenon can help dog owners recognize the signs and provide appropriate care for their pets.
Lactation, or the production of milk, in dogs is a natural process that occurs after they give birth to their puppies. However, there are several factors that can affect the ability of a dog to lactate. These factors include:
Read Also: Military Dog Handler Salary: How Much Do They Earn?
Overall, lactation in dogs is a complex process that can be influenced by various factors. Understanding and addressing these factors can help ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and her puppies.
While dogs may not be able to produce milk without being pregnant, there are several medical conditions that can cause lactation in non-pregnant dogs. These conditions include:
If you notice your dog producing milk without being pregnant, it is important to consult with a veterinarian. They can evaluate your dog’s health and determine the underlying cause of the lactation. Treatment will depend on the specific condition diagnosed.
Hormones play a crucial role in the production of milk in female dogs. When a dog is pregnant, her body releases hormones such as progesterone and prolactin, which prepare her mammary glands for milk production.
Progesterone, a hormone produced by the ovaries, helps regulate the growth and development of the mammary glands. It stimulates the cells in the glands to produce milk, and its levels increase significantly during pregnancy.
Prolactin, another hormone produced by the pituitary gland, is responsible for the synthesis and secretion of milk. Its levels rise towards the end of pregnancy, and it continues to stimulate milk production after the puppies are born.
Read Also: Effective Ways and Tips to Prevent Dog Chewing on Walls
These hormones work together to ensure that the mammary glands produce enough milk to nourish the puppies once they are born. Without the influence of these hormones, the mammary glands would not develop properly, and the dog would not be able to produce milk.
It is unlikely for a dog to produce milk without being pregnant or recently giving birth, as the production of milk requires the presence of these hormones. If a dog is producing milk without being pregnant, it could indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or medical condition, and a veterinarian should be consulted.
Abnormal milk production in dogs can be problematic and may require intervention to prevent complications. Here are some ways to prevent or manage abnormal milk production:
It is important to monitor your dog’s milk production and consult with a veterinarian if you notice any abnormalities. Timely intervention can help prevent complications and ensure the health and well-being of your dog.
Yes, dogs can produce milk even if they are not pregnant. This condition is known as false pregnancy or pseudopregnancy.
Dogs produce milk without being pregnant due to hormonal imbalances. False pregnancy can occur in dogs when their hormone levels are altered after they go through a heat cycle.
No, it is not normal for dogs to produce milk without being pregnant. However, it is a common phenomenon, especially in female dogs that have not been spayed.
Yes, dogs can nurse puppies even if they are not the biological mothers. This is often seen in cases where the puppies’ mother is unable to nurse or if the puppies are orphaned.
The duration of milk production in dogs without pregnancy can vary. It usually lasts for a few weeks to a month, but in some cases, it can persist for longer periods of time.
Can Dogs Smell Through Vacuum Sealed Bags Have you ever wondered if your furry friend can detect the scent of something sealed in a vacuum sealed bag? …
Read ArticleMost Expensive Dog Food When it comes to your furry friend, only the best will do. Treat your beloved pooch to the finest cuisine with our handpicked …
Read ArticleGoofy Dog Breed When it comes to dogs, there are many breeds to choose from, each with its own unique qualities. One of the most playful and lovable …
Read ArticleParvovirus Parvovirus is a highly contagious viral infection that can affect dogs of all ages, but it is particularly dangerous for puppies. It is …
Read ArticleCan Dogs Have Ascorbic Acid In Applesauce Dogs are lovable and cherished members of many families, and as responsible pet owners, we want to ensure …
Read ArticleCan I Use Genteal Tears On My Dog If you’re a dog owner, you know how important it is to take care of your furry friend’s health. But what if your dog …
Read Article