Pictures of Ruptured Cyst on Dog - What You Need to Know
Pictures Of Ruptured Cyst On Dog A ruptured cyst on a dog can be a cause of concern for pet owners. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on …
Read Article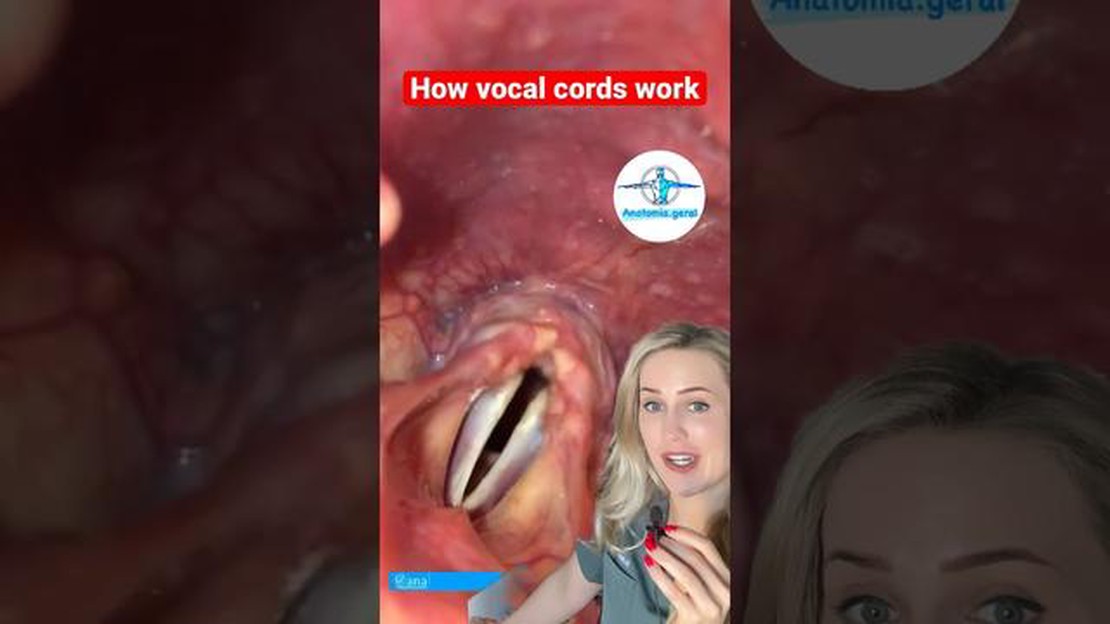
Dogs are known for their ability to communicate through barking, whining, and howling. However, excessive vocalization or certain behaviors can potentially damage a dog’s vocal cords. Understanding the potential risks is important for dog owners who want to ensure their pet’s vocal health.
One common way dogs can damage their vocal cords is through excessive barking. Continuous barking for prolonged periods of time can put strain on the vocal cords and lead to inflammation or even injury. This can occur if a dog is constantly barking at passersby, other animals, or in stressful situations.
Another risk for vocal cord damage in dogs is through laryngeal paralysis. This condition occurs when the muscles that control the movement of the vocal cords become weak or paralyzed. Dogs with this condition may have a hoarse or weak bark, difficulty breathing, or even complete loss of their bark. Laryngeal paralysis can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, trauma, or certain diseases.
Engaging in rough play or pulling on the leash during walks can also put strain on a dog’s vocal cords. Dogs who tug aggressively on their leash or play in a way that causes excessive strain or pulling on the neck can potentially damage their vocal cords. Owners should encourage gentle play and use appropriate training techniques to prevent injury.
In conclusion, while dogs are known for their vocal abilities, it is important for dog owners to be aware of the potential risks that can lead to damage to their pet’s vocal cords. Excessive barking, laryngeal paralysis, and rough play are all factors that can contribute to vocal cord damage. Taking preventative measures and seeking veterinary care when necessary can help maintain a dog’s vocal health and overall well-being.
Dogs have vocal cords just like humans do, and like any part of their body, they can be subject to damage or injury. While dogs are generally less prone to vocal cord damage compared to humans, it is still possible for them to experience issues with their vocal cords.
There are several potential ways that dogs can damage their vocal cords:
Signs of vocal cord damage in dogs may include hoarseness, changes in the sound of their bark, difficulty swallowing, or coughing. If you suspect your dog has injured their vocal cords, it is important to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Treatment for vocal cord damage in dogs will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the injury. In some cases, rest and supportive care may be enough for the vocal cords to heal on their own. In more severe cases, surgery or other interventions may be necessary.
To prevent vocal cord damage in dogs, it is important to manage their barking habits and avoid excessive or prolonged exercise. Providing appropriate chew toys and regularly inspecting their environment for potential hazards can also help reduce the risk of foreign object ingestion.
In conclusion, while vocal cord damage in dogs is less common compared to humans, it can still occur. Being aware of the potential risks and taking preventive measures can help keep your dog’s vocal cords healthy and functioning properly.
Dogs, like humans, have vocal cords that play a crucial role in their ability to produce sound and communicate. Understanding the anatomy of the vocal cords in dogs is important for identifying potential risks and complications that can occur.
Vocal Cord Function:
The vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are located within the larynx, which is part of the dog’s respiratory system. They are composed of mucous membranes and muscle tissue that vibrate when air passes through, producing sound.
Vocal Cord Structure:
The vocal cords consist of two thin, delicate folds of tissue that are stretched across the larynx. When the dog breathes in or out, the vocal cords come together or separate, allowing different pitches and tones of sound to be produced.
Read Also: Can I Cut Trifexis In Half: A Guide to Proper Medication Dosage for Dogs
Vocal Cord Health:
Healthy vocal cords in dogs should be smooth, flexible, and free of any abnormalities. However, certain factors can cause damage to the vocal cords, leading to changes in the dog’s voice or even complete loss of voice.
Potential Risks:
Various factors can potentially damage the vocal cords in dogs. Excessive barking, particularly at high volumes or for extended periods, can place strain on the vocal cords and cause inflammation or injury. Certain medical conditions, such as laryngeal paralysis or tumors, can also affect the function of the vocal cords.
Conclusion:
Understanding the anatomy of the vocal cords in dogs is essential for recognizing the potential risks and complications that can arise. Monitoring and managing a dog’s vocalization habits, as well as seeking veterinary attention for any vocal cord-related issues, can help maintain vocal cord health and ensure effective communication for your furry companion.
Read Also: Do Boxers Sleep A Lot: Unveiling Their Sleep Habits and Needs
In order to prevent vocal cord damage in dogs, it is important to provide them with proper training and socialization to reduce excessive barking. Using positive reinforcement techniques can also help to discourage pulling on the leash. Regular veterinary check-ups can detect and treat respiratory infections early, minimizing their impact on the vocal cords. Additionally, keeping dogs away from known irritants and providing a safe environment can reduce the risk of vocal cord damage.
If you suspect that your dog may have vocal cord damage, it is important to consult with a veterinarian. They can conduct a thorough examination and recommend appropriate treatment options to help alleviate the condition and prevent further damage to the vocal cords.
It is important for dog owners to recognize the signs of vocal cord injury in their pets. Dogs can damage their vocal cords through various actions such as excessive barking, trauma, or certain medical conditions. Here are some signs that may indicate a vocal cord injury in dogs:
If you notice any of these signs in your dog, it is important to seek veterinary care. A veterinarian can examine your dog’s vocal cords and determine the extent of the injury. They may recommend treatments such as rest, medication, or surgery, depending on the severity of the injury.
Note: It is important to note that not all vocal cord injuries in dogs are easily recognizable. Some injuries may require specialized tests or procedures to diagnose accurately. Therefore, if you suspect your dog has a vocal cord injury, it is best to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Vocal cord damage in dogs can lead to several potential risks if left untreated. These risks include:
It is important to seek veterinary care if you suspect your dog has vocal cord damage. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition and prevent further complications. Your veterinarian can provide guidance on the best course of action, which may include medication, surgery, or other interventions depending on the severity and underlying cause of the vocal cord damage.
Just like humans, dogs can also experience vocal health issues that may be caused by various factors. To ensure that your dog’s vocal health is protected and maintained, there are several steps you can take:
By following these tips, you can help protect and maintain your dog’s vocal health, ensuring they can communicate effectively without risking damage to their vocal cords.
Yes, dogs can damage their vocal cords by barking excessively. Over time, the strain and stress caused by constant barking can lead to inflammation and damage to the vocal cords.
The signs of vocal cord damage in dogs can vary, but common signs include changes in the dog’s bark, such as a hoarse or weak voice, difficulty barking or making unusual sounds, and coughing or choking during or after barking.
Vocal cord damage in dogs can be diagnosed through a thorough examination by a veterinarian. The vet may use a specialized scope to visualize the vocal cords and check for any abnormalities or signs of damage.
The potential risks of excessive barking for dogs include not only vocal cord damage, but also stress and anxiety, behavioral problems, physical exertion leading to fatigue and muscle strain, and potential harm to the dog’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Yes, vocal cord damage in dogs can be treated, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the damage. Treatment options may include medication, rest and rehabilitation, vocal exercises, and in extreme cases, surgical intervention.
Pictures Of Ruptured Cyst On Dog A ruptured cyst on a dog can be a cause of concern for pet owners. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on …
Read ArticleSpraying Dog With Water To Keep Cool Is your furry friend struggling to beat the heat this summer? We have the perfect solution! Introducing our …
Read ArticleRaining Cats And Dogs Crossword Are you a fan of word puzzles and crosswords? Do you love challenging your vocabulary and language skills? If so, then …
Read ArticleDog Depressed After Neuter How to Help a Dog Depressed After Neuter: Tips and Solutions Table Of Contents Recognizing Signs of Depression in a …
Read ArticleDo Pitbulls Get Along With Other Pitbulls Pitbulls are an incredibly popular breed of dog, known for their strength, loyalty, and protective nature. …
Read ArticleCan I Give My Dog Dramamine For Anxiety If you have a dog that experiences anxiety, you may be wondering if you can give them Dramamine to help calm …
Read Article