Are Huskies Stronger Than Pit Bulls? Evaluating Strength and Power in Dog Breeds
Are Huskies Stronger Than Pit Bulls When it comes to evaluating strength and power in dog breeds, there are many factors to consider. One of the most …
Read Article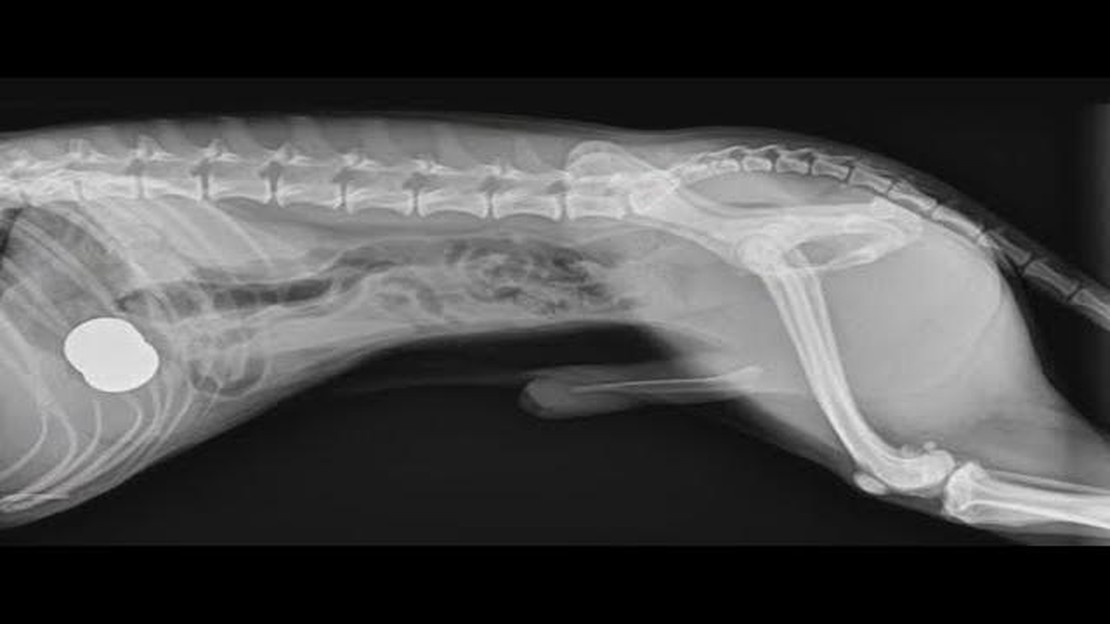
Dogs have a natural instinct to hunt and chase after small animals, and birds are no exception. Many dog owners have witnessed their furry friends catching birds and even devouring them. While this behavior may seem harmless or even entertaining, it raises the question: can a dog get sick from eating a bird?
The answer is yes, dogs can get sick from eating a bird, and there are several potential health risks associated with this behavior. One of the primary concerns is parasites. Birds like pigeons or sparrows may carry a variety of internal and external parasites, such as fleas, ticks, mites, or worms. If a dog ingests an infected bird, these parasites can transfer to the dog’s digestive system and potentially cause health issues.
Another concern is bacterial or viral infections. Birds can carry diseases, including avian influenza, salmonella, or campylobacteriosis, which can be transmitted to dogs through contact or ingestion. These infections can cause symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and in severe cases, even organ failure.
It is important for dog owners to be aware of these potential health risks and take preventative measures. This may include keeping the dog on a leash during walks to prevent them from chasing and catching birds, ensuring that the dog’s vaccinations are up to date, and regularly using flea and tick prevention products. If a dog does eat a bird, it is recommended to monitor their behavior and seek veterinary attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
While it is not uncommon for dogs to have the urge to chase and capture birds, it is important for pet owners to be aware of the potential risks associated with their furry friend consuming a bird.
Bacterial Infections: Birds can carry various bacteria, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, which can cause gastrointestinal issues in dogs. These bacteria can be present in the bird’s droppings, feathers, or even their internal organs. If a dog ingests a bird infected with these bacteria, they may experience symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and decreased appetite.
Viral Infections: Birds can also carry viral infections that can be transmitted to dogs. Avian influenza and West Nile virus are examples of viral infections that can be spread through contact with infected birds. Dogs exposed to these viruses may exhibit symptoms such as fever, respiratory issues, and lethargy.
Parasitic Infections: Birds can host parasites such as fleas, ticks, and mites. When a dog consumes a bird infested with these parasites, they can be transferred to the dog’s body, leading to potential infestations. Parasites can cause discomfort, itching, and in some cases, transmit diseases to the dog.
Physical Injuries: Hunting and capturing birds can put dogs at risk of physical injuries. Birds may defend themselves by pecking or scratching, which can cause wounds and potential infections. Additionally, if a dog chases a bird into an unsafe area, they may encounter hazards such as traffic or poisonous plants.
Poisoning: Some birds, such as pigeons, seagulls, and certain species of birds of prey, may consume poisoned bait or contaminated food. If a dog eats a bird that has ingested toxic substances, they may experience poisoning symptoms such as vomiting, seizures, and organ damage.
In conclusion, while it may be tempting to let your dog indulge in their natural instincts, it is essential to consider the potential risks associated with a dog consuming a bird. It is advisable to discourage dogs from chasing birds and to monitor their interactions with wildlife to ensure their safety and well-being.
Dogs are natural hunters, so it is not uncommon for them to chase and catch birds. While it can be an exciting playtime activity for your dog, there are potential health risks associated with them eating birds.
1. Salmonella and other bacterial infections: Birds can carry bacteria like Salmonella, Campylobacter, and E. coli, which can cause gastrointestinal infections in dogs. These bacteria can be present in the bird’s feces, feathers, or other parts of the bird that your dog may consume. Symptoms of bacterial infections include vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and lethargy.
2. Parasitic infections: Birds may harbor parasites like worms, mites, or ticks. Ingesting an infected bird can expose your dog to these parasites, leading to various health issues. Worm infestations can cause diarrhea, weight loss, and a dull coat, while mites and ticks can cause skin irritation or transmit other diseases.
3. Avian influenza: Avian influenza, also known as bird flu, is a viral infection that primarily affects birds but can occasionally transmit to mammals, including dogs. While the risk of transmission from birds to dogs is low, it is still a potential health concern. Symptoms of bird flu in dogs are similar to those in birds and may include respiratory issues, nasal discharge, lethargy, and fever.
4. Allergic reactions: Some dogs may develop allergic reactions to birds, especially if they are sensitive to feathers or bird dander. Allergic reactions can manifest as itching, redness, hives, or even respiratory difficulties. It is important to monitor your dog for any signs of allergies after they come into contact with birds.
5. Injury or obstruction: Depending on the size of the bird, there is a risk of injury or obstruction if your dog tries to swallow it whole or ingest bones. Sharp bird bones can cause internal injuries to the digestive tract, leading to pain, vomiting, or even a life-threatening condition called gastrointestinal obstruction.
Ultimately, while it may be challenging to prevent your dog from chasing birds, it is important to keep a close eye on them during outdoor activities and discourage them from eating birds. If you notice any unusual symptoms or suspect your dog has consumed a bird, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian for proper assessment and guidance.
When a dog eats a bird, there is a risk of transmitting various diseases and infections. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these potential health risks in order to take appropriate precautions and seek veterinary care if necessary.
Avian Influenza: Also known as bird flu, avian influenza is a viral infection that can affect both birds and mammals, including dogs. While it is rare for dogs to contract avian influenza from eating infected birds, it is still possible. Symptoms in dogs may include respiratory problems, fever, and digestive issues.
Salmonellosis: Birds, especially wild ones, may carry salmonella bacteria, which can cause salmonellosis in dogs. This bacterial infection can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and decreased appetite. It is important to note that salmonellosis can also be transmitted to humans, so proper hygiene is crucial when dealing with birds.
West Nile Virus: This mosquito-borne illness primarily affects birds, but dogs can also contract the virus. While the chances of a dog getting infected from eating a bird are low, it is still important to be cautious. Symptoms of West Nile virus in dogs can range from mild flu-like symptoms to more severe neurological issues.
Parasitic Infections: Birds can carry various parasites, such as fleas, ticks, mites, and lice. If a dog ingests an infected bird, these parasites can transfer to the dog and cause further health problems. It is essential to regularly check dogs for signs of parasites and use appropriate preventatives to keep them protected.
Read Also: Understanding Illinois Pitbull Laws: Everything You Need to Know
Internal Organ Damage: Depending on the size and condition of the bird ingested, there is a risk of internal organ damage. Sharp bones or beaks can cause perforations or obstructions in the dog’s digestive system, leading to serious health issues. Immediate veterinary attention is required if a dog exhibits symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, or lethargy after ingesting a bird.
While the risk of a dog getting sick from eating a bird may vary depending on the specific circumstances, it is crucial for dog owners to monitor their pets closely and consult a veterinarian if any concerning symptoms arise. Prevention is key, and keeping dogs away from dead birds and other wildlife is the best way to avoid potential health risks.
Read Also: Why Does My Dog Go Under The Bed and Cry: Understanding Canine Behavior
Dogs can potentially contract parasitic infestations from eating birds. Parasites that may be present in birds’ bodies include ticks, fleas, mites, and internal parasites like roundworms, tapeworms, or protozoa.
When a dog consumes a bird, these parasites can transfer to the dog’s digestive system or attach themselves to the dog’s skin. This can lead to various health issues and discomfort for the dog.
Ticks and Fleas:
Mites:
Internal parasites:
If you suspect that your dog has ingested a bird and is showing signs of parasitic infestation, it is important to consult with a veterinarian. They can perform diagnostic tests and provide appropriate treatment to eliminate any potential parasites and address any health issues.
While it is rare for birds to be poisonous and pose a direct threat to dogs, there are a few species of birds that can be toxic if ingested. These toxic birds are usually found in specific regions or habitats and are not commonly encountered by pet dogs. However, it is essential to be aware of these species and the potential risks they may pose to your furry friend.
1. Pitohui Birds: Found in New Guinea, the Pitohui birds are known to be the only documented poisonous birds in the world. These birds produce a potent neurotoxin called homobatrachotoxin, which is found in their skin and feathers. Ingesting even a small amount of this toxin can cause severe health issues in dogs, including muscle spasms, paralysis, respiratory distress, and even death.
2. Quaker Parrots: Quaker parrots, also known as Monk parakeets, are popular pet birds in some regions. While their toxicity is not well-documented, there have been reports of these birds consuming toxic plants, which can make their flesh and feces potentially harmful if ingested by dogs. It is essential to prevent dogs from eating the remains of a Quaker parrot or coming into contact with their droppings.
3. Birds of Prey: Some birds of prey, such as eagles, hawks, and owls, may consume prey that has been poisoned or exposed to toxic substances. If a dog ingests a bird of prey that has recently consumed a poisonous substance, it can lead to secondary poisoning in the dog. This secondary poisoning can cause various health issues, depending on the specific toxin involved.
4. Birds Fed a Poisonous Diet: In some cases, birds kept as pets or in aviaries may be fed a diet that includes toxic plants or substances. If a dog ingests a bird that has consumed a poisonous diet, the toxins may pass through the bird’s system and pose a risk to the dog. It is essential to keep pet birds away from toxic foods and plants and prevent dogs from accessing any birds that may have been inadvertently exposed.
In general, it is rare for dogs to encounter poisonous birds, and the risk of toxicity is relatively low. However, it is always best to be cautious and prevent dogs from consuming any unfamiliar or potentially toxic birds. If you suspect your dog has ingested a poisonous bird or is showing any signs of illness, it is recommended to seek veterinary assistance immediately.
When a dog eats a bird, there is a risk of bone fragments causing harm to their digestive system. Birds have small, delicate bones that can easily splinter when chewed on by a dog. These bone fragments can cause a range of issues for your dog, including damage to the throat, stomach, or intestines.
Choking hazards are also a concern when a dog eats a bird. If the bird is whole or a large piece is swallowed, it can become lodged in the dog’s throat, causing them to choke. Choking is a serious emergency that requires immediate attention.
To help prevent these risks, it is important to supervise your dog while they are eating and take away any bird carcasses or bones after they have finished. Additionally, avoid giving your dog cooked bones, as they are more likely to splinter and cause harm.
If you suspect that your dog has swallowed a bone or is choking, it is crucial to seek veterinary assistance right away. The vet may perform an x-ray to determine if there are any bone fragments or obstructions in your dog’s digestive tract. Prompt medical attention can help prevent potential complications and ensure your dog’s safety.
Yes, it is possible for a dog to get sick from eating a bird. While not all birds carry diseases that can be transmitted to dogs, there are certain risks to be aware of.
Some potential health risks for dogs that eat birds include contracting Salmonella or other bacterial infections, getting parasites such as worms or ticks, or having an allergic reaction to feathers.
To prevent your dog from getting sick if they eat a bird, it is best to discourage them from doing so in the first place. Additionally, make sure your dog is up to date on their vaccines and worming medications, and keep them away from birds that are sick or dead.
If your dog eats a bird, it is important to monitor their health and behavior afterward. If they show any signs of illness, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or lethargy, it is recommended to consult your veterinarian for further guidance.
No, not all birds are equally dangerous for dogs to eat. Some birds, such as pigeons or sparrows, are less likely to carry diseases compared to wild birds or birds of prey. However, it is still best to prevent your dog from eating any birds to avoid potential health risks.
While it is theoretically possible for a dog to get infected with Avian Influenza from eating birds, it is extremely rare. Avian influenza primarily affects birds and rarely crosses over to infect dogs or other mammals. However, caution should still be exercised to prevent dogs from consuming birds.
Are Huskies Stronger Than Pit Bulls When it comes to evaluating strength and power in dog breeds, there are many factors to consider. One of the most …
Read ArticleDog Urine Washing Machine Are you tired of dealing with the lingering smell of dog urine in your home? Look no further – introducing the Dog Urine …
Read ArticleAre Hounds Smart When it comes to dog intelligence, there is often a lot of debate. While certain breeds are praised for their problem-solving …
Read ArticleWhat Do Vets Do With Dead Dogs When a beloved pet passes away, their owners are left with the difficult task of making proper arrangements for their …
Read ArticleHow Much Is A Bath For A Dog At Petsmart Looking to give your furry friend a refreshing bath? Look no further than Petsmart! We offer professional …
Read ArticleCan Dogs See With Hair In Their Eyes When it comes to the topic of dogs and their vision, it is important to consider the role that hair plays in …
Read Article